SELECT 优化
KaiwuDB 支持使用 EXPLAIN 或 EXPLAIN ANALYZE 的输出,为 SELECT 优化提供支持的信息。目前,KaiwuDB 支持以下 SELECT 优化策略:
- 级别越少,查询速度越快。
- 重组查询以减少处理级别通常会提高性能。避免扫描整个表,这是访问数据最慢的方式。可以通过创建至少包含查询在其
WHERE子句中筛选的列之一的索引来避免这种情况。
基于 EXPLAIN 语句的输出,KaiwuDB 支持使用以下方式确定是否需要进行全表扫描查询:
- 查看
Field属性值为table的行的Description值,获取查询使用的索引。 - 查看
Field属性值为spans的行的Description值,获得索引中需要被扫描的Key值范围。
EXPLAIN
EXPLAIN 语句返回 KaiwuDB 可解释语句的查询计划。用户可以使用这些信息来优化查询。
所需权限
- 非三权分立模式下,用户需要对所解释的语句具有适当的权限。
- 三权分立模式下,普通用户需要对所解释的语句具有适当的权限。
语法格式
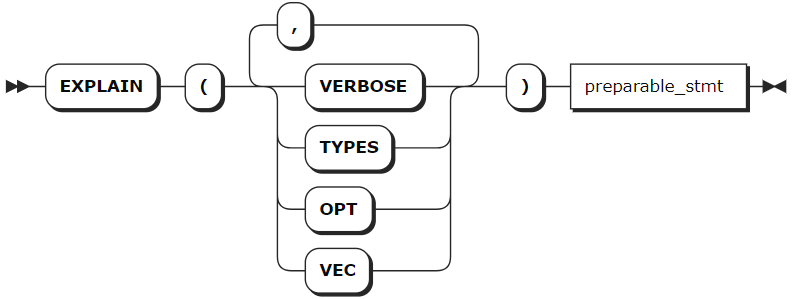
preparable_stmt
参数说明
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
VERBOSE | 显示尽可能多的查询计划信息。 |
TYPES | 包括 KaiwuDB 选择用来计算中间 SQL 表达式的数据类型。 |
OPT | 查看由基于成本的优化器(Cost-Based Optimizer, COB)生成的查询计划树。OPT 和 VERBOSE 关键字用于查看优化器在规划查询时使用的成本的详细信息。OPT 和 TYPES 关键字用于查看成本和类型的详细信息。 |
VEC | 查看有关查询的矢量化执行计划的详细信息。如果查询的表包含不支持的数据类型,则返回未处理的数据类型错误。 说明 默认情况下,禁用矢量化执行引擎。如需开启,需运行 SET vectorize = on 命令。 |
preparable_stmt | 需要进行 EXPLAIN 操作的语句。基本上,所有语句都可以和 EXPLAIN 组合使用,例如 CREATE、INSERT、UPDATE、DELETE 等。 |
返回结果字段说明
执行成功的 EXPLAIN 语句将返回具有以下字段的表:
- Tree:查询计划的层次结构的树状表示形式。
- Field:查询计划的属性名称。分布式和向量化的属性适用于整个查询计划。所有其他属性应用于树列中的查询计划节点。
- Description:有关字段中参数的附加信息。
- Columns:提供给层次结构较低层的流程的列,包含在类型和详细的输出中。
- Ordering:结果在层次结构的每一层呈现给流程的顺序,以及结果集在每一层的其他属性。该字段包含在使用 TYPES 和 VERBOSE 选项的输出结果中。
语法示例
以下示例假设已创建 accounts、accounts_type 表并写入相关数据。
-- 创建 accounts 表。
CREATE TABLE accounts(id INT8 DEFAULT unique_rowid() PRIMARY KEY, balance DECIMAL);
CREATE TABLE
-- 创建 accounts_type 表。
CREATE TABLE accounts_type(id INT8 DEFAULT unique_rowid(),balance DECIMAL, data_type INT);
CREATE TABLE
不使用任何参数的
EXPLAIN语句。EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM accounts; tree|field |description ----+-----------+---------------- |distributed|true |vectorized |false scan| | |table |accounts@primary |spans |FULL SCAN (5 rows)在连接查询上使用
EXPLAIN语句。EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM accounts AS a JOIN accounts_type AS b ON a.id=b.id; tree |field |description ---------+-----------------+--------------------- |distributed |true |vectorized |false hash-join| | │ |type |inner │ |equality |(id) = (id) │ |left cols are key| ├── scan| | │ |table |accounts@primary │ |spans |FULL SCAN └── scan| | |table |accounts_type@primary |spans |FULL SCAN (12 rows)使用
VERBOSE选项的EXPLAIN语句。EXPLAIN(VERBOSE) SELECT * FROM accounts; tree|field |description |columns |ordering ----+-----------+----------------+-------------+-------- |distributed|true | | |vectorized |false | | scan| | |(id, balance)| |table |accounts@primary| | |spans |FULL SCAN | | (5 rows)使用
TYPES选项的EXPLAIN语句。EXPLAIN(TYPES) SELECT * FROM accounts; tree|field |description |columns |ordering ----+-----------+----------------+-------------------------+-------- |distributed|true | | |vectorized |false | | scan| | |(id int, balance decimal)| |table |accounts@primary| | |spans |FULL SCAN | | (5 rows)使用
OPT选项的EXPLAIN语句。EXPLAIN(OPT) SELECT * FROM accounts WHERE id > 2 ORDER BY balance DESC; text --------------------------------- sort └── scan accounts └── CONSTRAINT: /1: [/3 - ] (3 rows)使用
OPT、VERBOSE组合的EXPLAIN语句。EXPLAIN(OPT, VERBOSE) SELECT * FROM accounts WHERE id > 2 ORDER BY balance DESC; text --------------------------------------------------------------------- sort ├── columns: id:1 balance:2 ├── stats: [rows=333.333333, distinct(1)=333.333333, null(1)=0] ├── cost: 409.225479 ├── key: (1) ├── fd: (1)-->(2) ├── ordering: -2 ├── prune: (2) ├── interesting orderings: (+1) └── scan accounts ├── columns: id:1 balance:2 ├── CONSTRAINT: /1: [/3 - ] ├── stats: [rows=333.333333, distinct(1)=333.333333, null(1)=0] ├── cost: 346.676667 ├── key: (1) ├── fd: (1)-->(2) ├── prune: (2) └── interesting orderings: (+1) (18 rows)使用
OPT、TYPES组合的EXPLAIN语句。EXPLAIN(OPT, TYPES) SELECT * FROM accounts WHERE id > 2 ORDER BY balance DESC; text --------------------------------------------------------------------- sort ├── columns: id:1(int!null) balance:2(decimal) ├── stats: [rows=333.333333, distinct(1)=333.333333, null(1)=0] ├── cost: 409.225479 ├── key: (1) ├── fd: (1)-->(2) ├── ordering: -2 ├── prune: (2) ├── interesting orderings: (+1) └── scan accounts ├── columns: id:1(int!null) balance:2(decimal) ├── CONSTRAINT: /1: [/3 - ] ├── stats: [rows=333.333333, distinct(1)=333.333333, null(1)=0] ├── cost: 346.676667 ├── key: (1) ├── fd: (1)-->(2) ├── prune: (2) └── interesting orderings: (+1) (18 rows)使用
VEC选项的EXPLAIN语句。SET vectorize = on; SET EXPLAIN(VEC) SELECT * FROM accounts WHERE id > 2; text ------------------------- │ └ Node 1 └ *colexec.colBatchScan (3 rows)使用
EXPLAIN语句获取查询使用的索引和键,判定是否进行了全表扫描。-- 1. 创建表 CREATE TABLE explain_test (k INT PRIMARY KEY, v INT); CREATE TABLE -- 2. 由于 v 列没有索引,查询 v 列时会扫描全表。 EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM explain_test WHERE v BETWEEN 4 AND 5; tree|field |description ----+-----------+--------------------- |distributed|true |vectorized |false scan| | |table |explain_test@primary |spans |FULL SCAN |filter |(v >= 4) AND (v <= 5) (6 rows) -- 3. 在 v 列上创建索引。 CREATE INDEX index_v ON explain_test (v); CREATE INDEX -- 4. 查询时避免了全表扫描。 EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM explain_test WHERE v BETWEEN 4 AND 5; tree|field |description ----+-----------+-------------------- |distributed|false |vectorized |false scan| | |table |explain_test@index_v |spans |/4-/6 (5 rows)
EXPLAIN ANALYZE
EXPLAIN ANALYZE 语句用于执行 SQL 查询,生成包含查询详细信息的文件。这些信息用于定位查询花费时间的具体部分,以及根据输入规范处理输入行流并对其进行处理的组件的运行时长,从而解决查询较慢的问题。
所需权限
用户需要对所解释的语句具有适当的权限。
语法格式
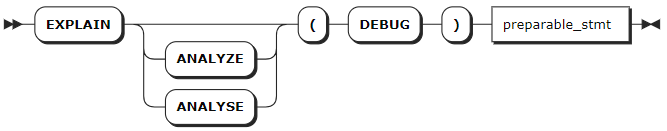
preparable_stmt
参数说明
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
preparable_stmt | 需要进行 EXPLAIN ANALYZE 操作的语句。基本上,所有语句都可以和 EXPLAIN ANALYZE 组合使用,例如 CREATE、INSERT、UPDATE、DELETE 等。 |
语法示例
使用 EXPLAIN ANALYZE 语句执行 SELECT 查询。
EXPLAIN ANALYZE(DEBUG) SELECT * FROM accounts WHERE id > 2 ORDER BY balance DESC;
text
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Statement diagnostics bundle generated. Download from the Admin UI (Advanced
Debug -> Statement Diagnostics History), via the direct link below, or using
the command line.
Admin UI: http://127.0.0.1:8080
Direct link: http://127.0.0.1:8080/_admin/v1/stmtbundle/857952323520757761
Command line: kwbase statement-diag list / download
(6 rows)