Connect to KWDB using Hibernate
Hibernate is a widely used Object-Relational Mapping (ORM) framework that simplifies database persistence operations in Java applications. It allows developers to interact with databases using Java objects without writing extensive SQL code.
KWDB provides a dedicated Dialect specifically designed for its database system, defining its SQL dialect specifications to ensure Hibernate generates compatible SQL queries for KWDB's database engines.
With KWDB's Hibernate integration, developers can:
- Connect to KWDB databases using the familiar Hibernate framework within Spring Boot projects
- Leverage Java Persistence API (JPA) for standardized database operations
- Perform data querying, writing, and deletion operations using object-oriented paradigms
- Utilize standard Hibernate features while working with KWDB
Prerequisites
- OpenJDK 1.8 or higher installed
- Maven 3.6 or higher installed
- Spring Boot 2.3.2 or higher installed
- KaiwuDB JDBC driver package obtained
- KaiwuDB-adapted Hibernate Core 5.6.16 package
- KWDB version 2.0.4 or higher installed and running with:
- Properly configured database authentication
- A database created for your connection
- A user with appropriate privileges on tables or higher
Environment Setup
In your project directory, create a
pom.xmlfile and include the dependencies for JPA, Hibernate, and KaiwuDB JDBC driver:<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.3.2.RELEASE</version> <relativePath/> </parent> <groupId>com.kaiwudb.hibernate</groupId> <artifactId>kwdb-hibernate</artifactId> <version>1.0</version> <name>kwdb-hibernate</name> <packaging>pom</packaging> <description>This program is use kaiwudb jdbc test hibernate framework example.</description> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding> <maven.compiler.encoding>UTF-8</maven.compiler.encoding> <maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source> <maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target> <maven.compiler.version>3.8.1</maven.compiler.version> <java.version>1.8</java.version> </properties> <modules> <module>relational</module> <module>time-series</module> </modules> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <!-- jpa --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId> <exclusions> <exclusion> <groupId>org.hibernate</groupId> <artifactId>hibernate-core</artifactId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency> <!-- hibernate-core --> <dependency> <groupId>org.hibernate</groupId> <artifactId>hibernate-core</artifactId> <version>5.6.16.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <!-- kaiwudb-jdbc--> <dependency> <groupId>com.kaiwudb</groupId> <artifactId>kaiwudb-jdbc</artifactId> <version>3.1.0</version> </dependency> <!-- mockito-core --> <dependency> <groupId>org.mockito</groupId> <artifactId>mockito-core</artifactId> <version>2.19.1</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> </project>If the KaiwuDB JDBC driver cannot be loaded, run the following command to install the driver into your local Maven repository:
mvn install:install-file "-Dfile=../kaiwudb-jdbc-3.1.0.jar" "-DgroupId=com.kaiwudb" "-DartifactId=kaiwudb-jdbc" "-Dversion=3.1.0" "-Dpackaging=jar"Install the KaiwuDB-adapted Hibernate Core package into your local Maven repository:
Example:
mvn install:install-file "-Dfile=../hibernate-core-5.6.16.RELEASE.jar" "-DpomFile=../hibernate-core-5.6.16.RELEASE.pom" "-DgroupId=org.hibernate -DartifactId=hibernate-core" "-Dversion=5.6.16.RELEASE" "-Dpackaging=jar"
Database Configuration and Usage
The configuration and usage involve the following steps:
Configure the data source: Specify the database dialect and other connection properties. For time-series databases, transaction management must be disabled.
Define entity classes: These classes map to database tables and data types. Entity classes typically use JPA annotations to specify table names and field mappings.
Define data access interfaces: These interfaces define interactions with the database, including queries and updates.
Define service interfaces and implementations: The service layer encapsulates data access operations and provides unified business logic interfaces and handling methods for applications.
Define the controller layer: The controller layer handles incoming user requests, invokes the appropriate service methods to execute business logic, and returns the processed results to the user.
KWDB supports both time-series and relational databases, each with specific configuration requirements.
Time-Series Databases
Note
For time-series data, KWDB supports explicit transactions for queries and writes, but does not support transaction-based DDL operations. To ensure proper functionality, transaction management must be disabled when working with time-series operations.
In the
application.ymlfile under theresourcesdirectory, configure the data source, disable transaction management, and specify the dialect package.Example:
spring: datasource: driver-class-name: com.kaiwudb.Driver url: jdbc:kaiwudb://127.0.0.1:26257/test_tsdb username: <user_name> password: <password> jpa: properties: Disable transaction management javax.persistence.transactionType: RESOURCE_LOCAL open-in-view: false hibernate: ddl-auto: update show-sql: true database-platform: org.hibernate.dialect.KaiwuDBDialect server: port: 9001Define the entity class in the
entitydirectory, for exampleTsdbEntity.java.Example:
In this example, the name value in the
@Tableannotation (tsdb_table) corresponds to the time-series table in KWDB. Each field maps to a currently supported data type. Thet1column serves as the primary tag column in the time-series table.@Data @Entity @Table(name = "tsdb_table") public class TsdbEntity { @Id @JsonFormat(shape = JsonFormat.Shape.STRING, pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS", timezone = "GMT+8") private Timestamp ts; private Short c1; private Integer c2; private Long c3; private Float c4; private Double c5; private Boolean c6; private String c7; private String c8; private String c9; private String c10; private String c11; @JsonFormat(shape = JsonFormat.Shape.STRING, pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS", timezone = "GMT+8") private Timestamp c12; private Integer t1; }Define the data access layer in the
repositorydirectory.Example:
@Repository public interface TsdbEntityRepository extends JpaRepository<TsdbEntity, Timestamp> { TsdbEntity findByT1AndTs(@Param("t1") int t1, @Param("ts") Timestamp ts); List<TsdbEntity> findAll(); }Define the Service interface and implementation.
Define the Service interface in the
servicedirectory.Example:
public interface TsdbService { int insert(TsdbEntity entity); int delete(int t1, String ts); TsdbEntity findByT1AndTs(int t1, String ts) throws Exception; List<TsdbEntity> findList(); }Define the implementation in the
service/impldirectory.Note
For time-series databases, we implement
INSERTandDELETEoperations usingJdbcTemplateinstead of JPA because JPA requires transaction management, which is not supported for time-series DDL operations in KWDB.Example:
@Service class TsdbServiceImpl implements TsdbService { @Autowired private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; @Autowired private TsdbEntityRepository repository; @Override public int insert(TsdbEntity entity) { String sql = "INSERT INTO tsdb_table (ts, c1, c2, c3, c4, c5, c6, c7, c8, c9, c10, c11, c12, t1) VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)"; return jdbcTemplate.update(sql, entity.getTs(), entity.getC1(), entity.getC2(), entity.getC3(), entity.getC4(), entity.getC5(), entity.getC6(), entity.getC7(), entity.getC8(), entity.getC9(), entity.getC10(), entity.getC11(), entity.getC12(), entity.getT1()); } @Override public int delete(int t1, String ts) { String sql = "DELETE FROM tsdb_table WHERE t1 = ? AND ts = ?"; return jdbcTemplate.update(sql, t1, ts); } @Override public TsdbEntity findByT1AndTs(int t1, String ts) throws Exception { SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS"); return repository.findByT1AndTs(t1, new Timestamp(sdf.parse(ts).getTime())); } @Override public List<TsdbEntity> findList() { return repository.findAll(); } }
Define the controller in the
controllerdirectory.Example:
@RestController @RequestMapping("tsdb") public class TsdbController { @Autowired private TsdbService service; @PostMapping("add") public String add(@RequestBody TsdbEntity entity) { try { if (entity == null) { return ""Failed to receive time-series data!"; } if (entity.getTs() == null || entity.getT1() == null) { return "Timestamp and tag columns cannot be null!"; } int rows = service.insert(entity); if (rows < 1) { return "Failed to add time-series data!"; } return "Successfully added time-series data. Rows affected: " + rows; } catch (Exception e) { return e.getMessage(); } } @DeleteMapping("delete") public String delete(@RequestParam(value = "t1") Integer t1, @RequestParam(value = "ts") String ts) { try { int rows = service.delete(t1, ts); if (rows < 1) { return "Failed to delete time-series data!"; } return "Successfully deleted time-series data. Rows affected: " + rows; } catch (Exception e) { return e.getMessage(); } } @GetMapping("get") public TsdbEntity get(@RequestParam(value = "t1") Integer t1, @RequestParam(value = "ts") String ts) throws Exception { return service.findByT1AndTs(t1, ts); } @GetMapping("list") public List<TsdbEntity> list() { return service.findList(); } }Verify data operations.
- Adding data
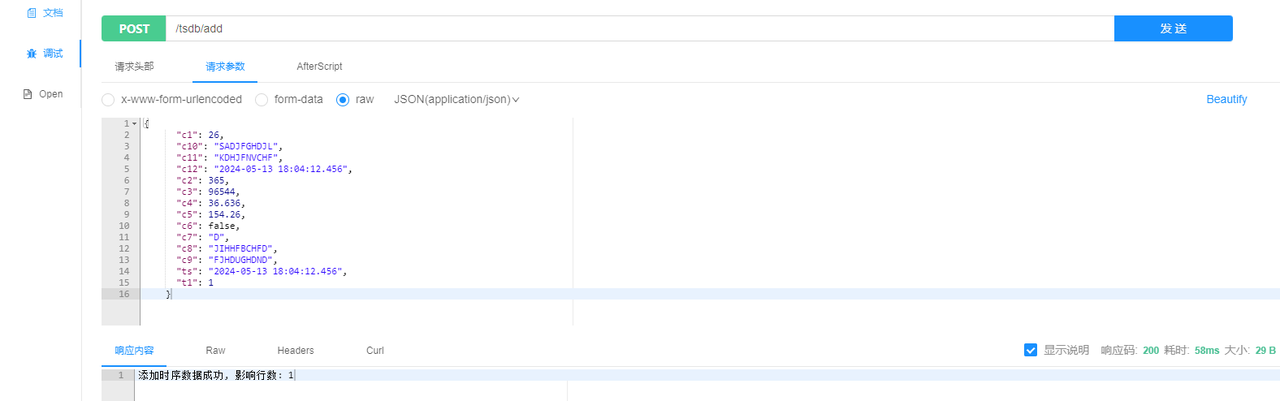
- Deleting data
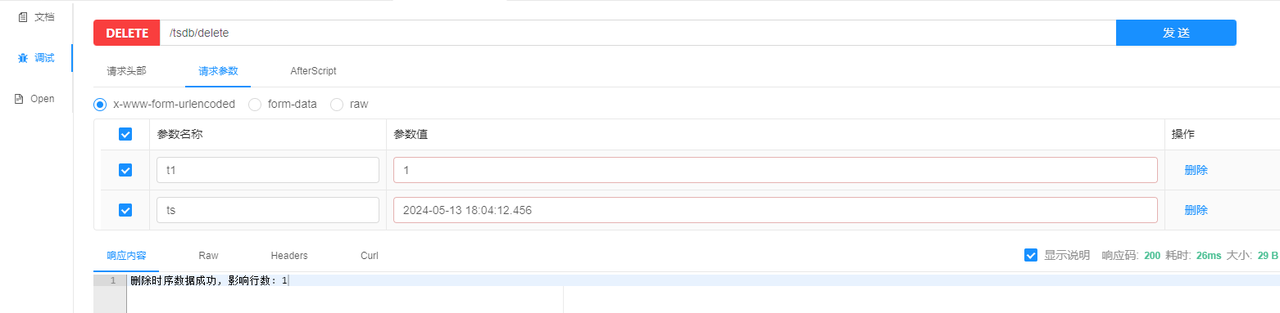
- Querying data by the primary tag and timestamp
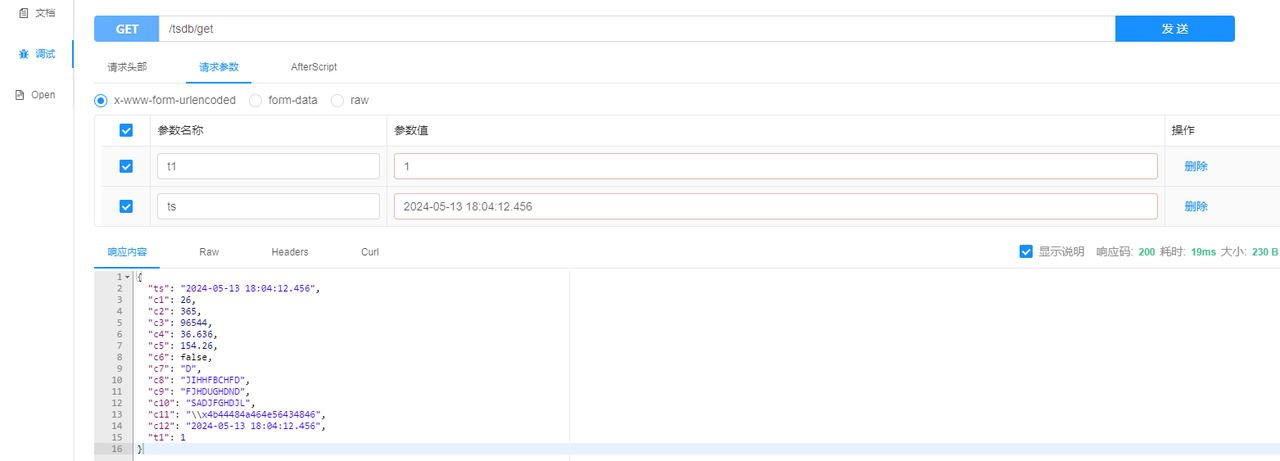
- Querying full dataset
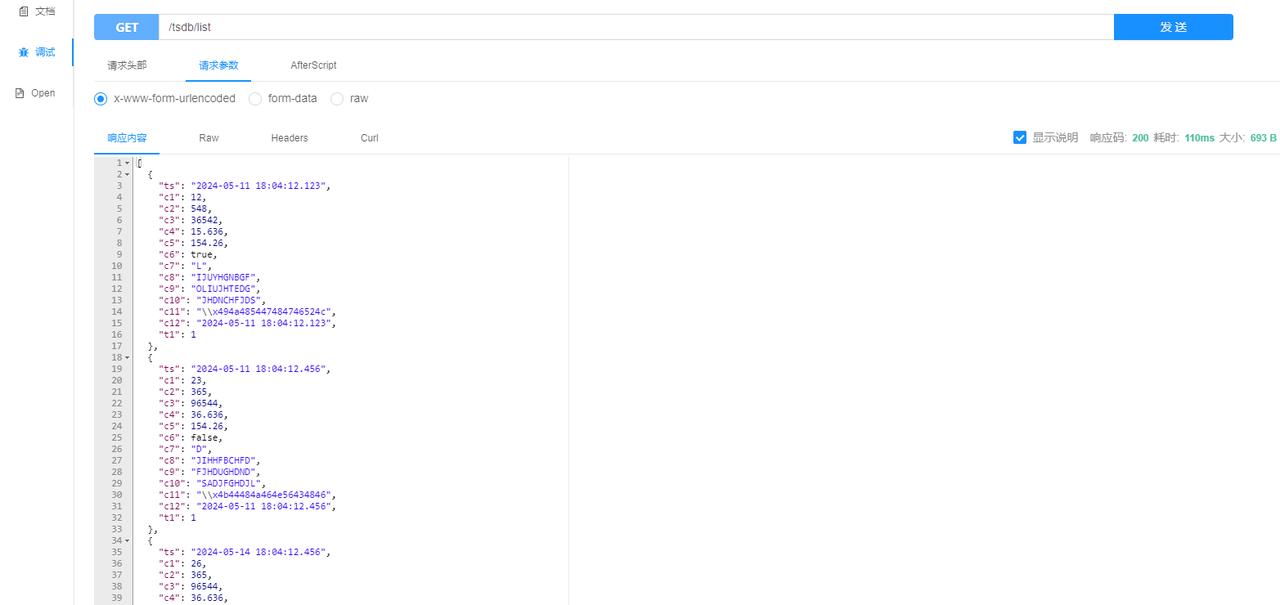
- Adding data
Relational Databases
In the
application.ymlfile under theresourcesdirectory, configure the data source and specify the dialect package.Example:
spring: datasource: driver-class-name: com.kaiwudb.Driver url: jdbc:kaiwudb://127.0.0.1:26257/test_rdb username: <user_name> password: <password> jpa: open-in-view: false hibernate: ddl-auto: update show-sql: true database-platform: org.hibernate.dialect.KaiwuDBDialect server: port: 9002In the
entitydirectory, define the entity class that maps to the relational table, for exampleRdbEntity.java.Example:
In this example, the
namevalue in the@Tableannotation (rdb_table) corresponds to the relational table in KWDB. Each field maps to a supported data type. Theidfield uses a SEQUENCE for automatic generation, so the following annotations are required:@SequenceGenerator(name = "sequence", sequenceName = "rdb_table_id", allocationSize = 1) @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.SEQUENCE, generator = "sequence")@Data @Entity @Table(name = "rdb_table") @SequenceGenerator(name = "sequence", sequenceName = "rdb_table_id", allocationSize = 1) public class RdbEntity { @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.SEQUENCE, generator = "sequence") private Integer id; private Short c1; private Integer c2; private Long c3; private Float c4; private Double c5; private Boolean c6; private String c7; private String c8; private String c9; private String c10; private String c11; @JsonFormat(shape = JsonFormat.Shape.STRING, pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS", timezone = "GMT+8") private Timestamp c12; }The SQL needed to create the relational table and sequence is as follows:
CREATE SEQUENCE rdb_table_id START 1 INCREMENT 1; CREATE TABLE test_rdb.rdb_table ( id int PRIMARY KEY DEFAULT nextval('rdb_table_id'), c1 smallint, c2 int, c3 bigint, c4 float4, c5 float8, c6 bool, c7 char(1), c8 nchar(10), c9 varchar(10), c10 nvarchar(10), c11 bytes, c12 timestamp );Define the data access layer in the
repositorydirectory.Example:
@Repository public interface RdbEntityRepository extends JpaRepository<RdbEntity, Integer> { @Override <S extends RdbEntity> S saveAndFlush(S entity); @Override void deleteInBatch(Iterable<RdbEntity> list); RdbEntity getById(@Param("id") Integer id); List<RdbEntity> findAll(); }Define the Service interface and implementation.
Create the Service interface in the
servicedirectory.Example:
public interface RdbService { RdbEntity save(RdbEntity entity); void delete(List<RdbEntity> list); RdbEntity findById(Integer id); List<RdbEntity> findList(); }Create the implementation in the
service/impldirectory.Example:
@Service class RdbServiceImpl implements RdbService { @Autowired private RdbEntityRepository repository; @Override public RdbEntity save(RdbEntity entity) { return repository.saveAndFlush(entity); } @Override public void delete(List<RdbEntity> list) { repository.deleteInBatch(list); } @Override public RdbEntity findById(Integer id) { return repository.getById(id); } @Override public List<RdbEntity> findList() { return repository.findAll(); } }
Define the Controller in the
controllerdirectory.Example:
@RestController @RequestMapping("rdb") public class RdbController { @Autowired private RdbService service; @PostMapping("add") public String add(@RequestBody RdbEntity entity) { try { if (entity == null) { return "Failed to receive relational data!"; } return "Successfully added relational data:\n " + Json.pretty(service.save(entity)); } catch (Exception e) { return e.getMessage(); } } @DeleteMapping("delete") public String delete(@RequestParam(value = "id") Integer id) { try { RdbEntity entity = service.findById(id); if (entity == null) { return "Relational data does not exist."; } service.delete(Collections.singletonList(entity)); return "Successfully deleted relational data."; } catch (Exception e) { return e.getMessage(); } } @GetMapping("get") public RdbEntity get(@RequestParam(value = "id") Integer id) throws Exception { return service.findById(id); } @GetMapping("list") public List<RdbEntity> list() { return service.findList(); } }Verify data operations.
- Adding data

- Deleting data
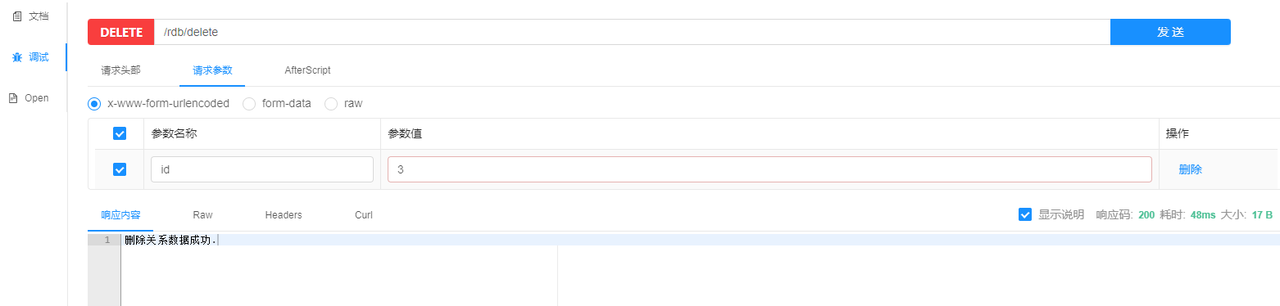
- Querying data by ID
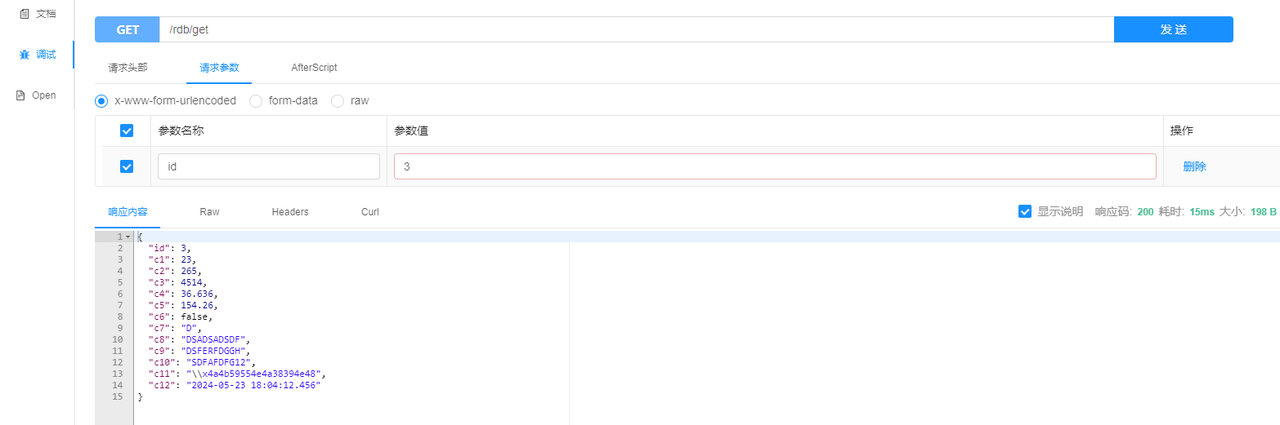
- Querying full dataset
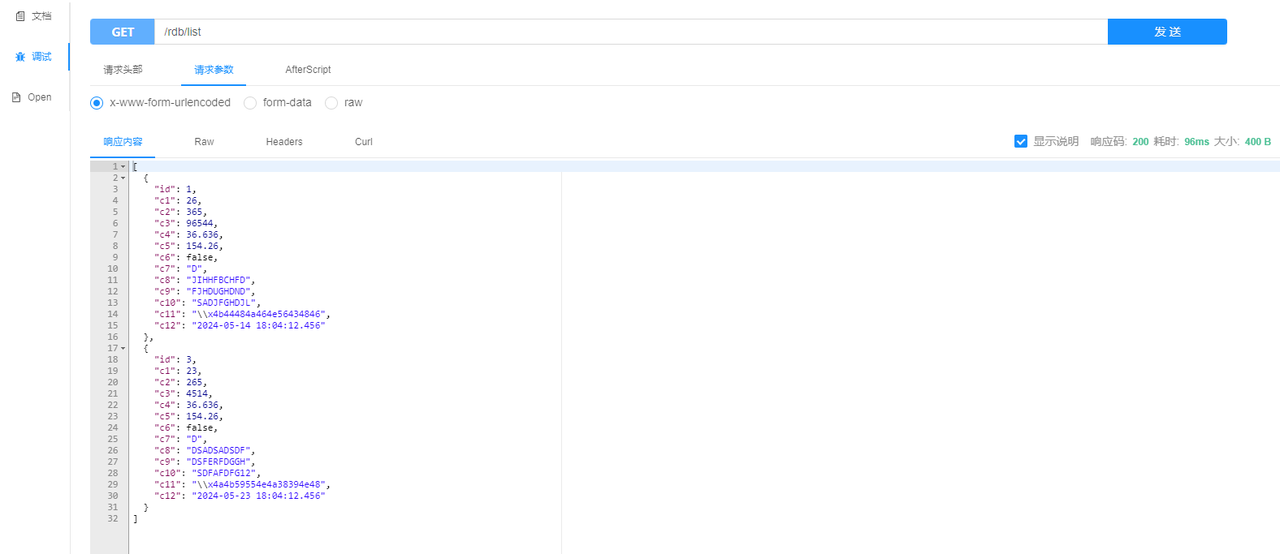
- Adding data