Schedules
Schedules are specified jobs that are automatically executed based on the pre-defined time or event.
KWDB supports the following statements:
CREATE SCHEDULE: create a schedule.SHOW SCHEDULE: view the scheduling period, execution time, and execution status of schedules.SHOW JOBS FOR SCHEDULE: view the start time, end time, execution progress, execution results, error messages of jobs executed in the history and current periods. For details, see SHOW JOBS.ALTER SCHEDULE: change the scheduling period, the error handling policy for a running schedule, or the handling policy for a previous schedule that has not yet been executed.PAUSE SCHEDULE: pause a schedule.RESUME SCHEDULE: resume a paused schedule.DROP SCHEDULE: remove a schedule.
By default, KWDB scans the schedule list every 60 seconds and randomly gets and executes 10 schedules. You can use the SET CLUSTER SETTING <parameter> = <value> statement to set the following cluster settings:
jobs.scheduler.enabled: enable or disable a schedule. By default, it is set toTRUE, which means to enable a schedule.jobs.scheduler.pace: set how often to schedule thesystem.scheduled_jobstable. By default, it is set to60seconds. It is recommended not to set a value that is smaller than60s. If you set a value that is smaller than60s, the system will adopt the default value (60s).jobs.scheduler.max_jobs_per_iteration: set the maximum number of schedules to be scanned each time. By default, it is set to10. If it is set to0, it means no limit on the number of schedules.
CREATE SCHEDULE
The CREATE SCHEDULE statement creates a schedule.
Privileges
The user must be a member of the admin role. By default, the root user belongs to the admin role.
Syntax
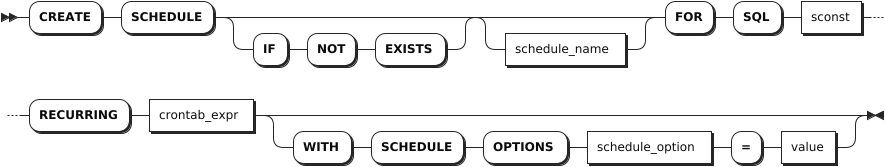
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
IF NOT EXISTS | Optional. - When the IF NOT EXISTS keyword is used, the system creates a new schedule only if a schedule of the same name does not already exist. Otherwise, the system fails to create a new schedule without returning an error. - When the IF NOT EXISTS keyword is not used, the system creates a new schedule only if a schedule of the same name does not already existed. Otherwise, the system fails to create a new schedule and returns an error. |
schedule_name | Optional. The name of the schedule to create. If no name is specified, the system will automatically generate a name, such as EXEC SQL 1718951529. The schedule name must be unique within the database. The schedule name can be entered as a string literal but does not support pure digits. When the IF NOT EXISTS keyword is used, you must specify a name for a schedule. |
sconst | The specified SQL statements. Currently, KWDB only supports INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE statements for a schedule. The SQL statements need to specify a database and tables. |
RECURRING crontab_expr | The recurring expression to execute a schedule. Available recurring expressions: - 7-field expression, also known as full-field expression: fields are separated using spaces ( <seconds> <minutes> <hours> <day-of-month> <month> <day-of-week> <year>), where the seconds field is pre-set to 0, indicating to execute the schedule for at 0 second. - 6-field expression: fields are separated using spaces ( <minutes> <hours> <day-of-month> <month> <day-of-week> <year>), where the year field is pre-set to *, indicating to execute the schedule for every year. - 5-field expression: fields are separated using spaces ( <minutes> <hours> <day-of-month> <month> <day-of-week>) - Pre-defined expressions include @annually (run a schedule once a year at midnight on the first day of January), @yearly (run a schedule once a year at midnight on the first day of January, same to @annually), @monthly (run a schedule once a month at midnight on the first day of the month ), @weekly (run a schedule once a week at midnight every Sunday), @daily (run a schedule once a day at midnight), @hourly (run hourly)For details about Crontab expression, see Crontab Expression. |
schedule_option | The options to execute a schedule. Available options: first_run: execute the schedule at the specified time. If not specified, execute the schedule based on the RECURRING expression by default. Support using TIMESTAMPTZ and NOW. on_execution_failure: if an error occurs during the schedule execution, do the following: - retry: retry the schedule right away. - pause: pause the schedule. This requires to manually resume the schedule. - reschedule: (Default) retry the schedule based on the RECURRING expression. on_previous_running: if the previous schedule is still running, do the following: - start: start the new schedule anyway, even if the previous one is still running. - skip: skip the new schedule. - wait: (Default) wait for the previous schedule to complete and then run the new schedule. |
Crontab expression
| Field | Value Range | Special Character | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
seconds | [0, 59] |
|
|
minutes | [0, 59] |
| |
hour | [0, 23] |
| |
day of month | [1, 31] |
| |
month | [1,12]or JAN-DEC |
| |
day of week | [0,7]or SUN-SAT. Both 0 and 7 indicate Sunday, compatible with Linux crontab. |
| |
year | [1970, 2099] |
|
Examples
This example creates a schedule named s1, which inserts data of the tsdb.t1 table into the tsdb.t2 table every hour.
CREATE SCHEDULE s1 FOR SQL 'INSERT INTO tsdb.t2 SELECT * FROM tsdb.t1' RECURRING '@hourly' WITH SCHEDULE OPTIONS first_run=NOW;
SHOW SCHEDULES
The SHOW SCHEDULE statement lists created schedules. By default, the system automatically creates the scheduled_table_retention schedules.
Privileges
The user must be a member of the admin role. By default, the root user belongs to the admin role.
Syntax
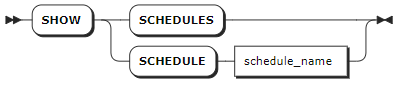
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
schedule_name | The name of the schedule to view. |
Responses
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
id | The ID of the schedule. |
name | The name of the schedule. |
schedule_status | The status of the schedule. |
next_run | The TIMESTAMP at which the next schedule to run. |
state | Keep it as empty. Display last-known errors about the schedule, or messages about how to deal with the errors. |
recurrence | How often the schedule runs. |
jobsrunning | The number of jobs currently running for the schedule. |
owner | The user who creates the schedule. |
created | The TIMESTAMP when the schedule was created. |
command | The SQL command that the schedule will run. |
Examples
Show details about schedules created by the system.
show schedules; id | name | schedule_status | next_run | state | recurrence | jobsrunning | owner | created | command ---------------------+----------------------------+-----------------+---------------------------+-------+------------+-------------+-------+----------------------------------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 958737479282262017 | scheduled_table_statistics | ACTIVE | 2024-04-09 10:00:00+00:00 | | @hourly | 0 | root | 2024-04-09 09:10:58.995182+00:00 | {"insert_statement": "INSERT INTO ts_table VALUES ('2023-07-13 14:06:32.272', 10.2, 219, 0.32, 1,1)"} (1 row)Show details about a specified schedule.
show schedule scheduled_table_statistics; id | name | schedule_status | next_run | state | recurrence | jobsrunning | owner | created | command ---------------------+----------------------------+-----------------+---------------------------+-------+------------+-------------+-------+----------------------------------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 958737479282262017 | scheduled_table_statistics | ACTIVE | 2024-04-09 10:00:00+00:00 | | @hourly | 0 | root | 2024-04-09 09:10:58.995182+00:00 | {"insert_statement": "INSERT INTO ts_table VALUES ('2023-07-13 14:06:32.272', 10.2, 219, 0.32, 1,1)"} (1 row)
ALTER SCHEDULE
The ALTER SCHEDULE statement changes an existing schedule. The changes take effect at the next scheduling time and do not affect the status of the currently running jobs or schedules.
Privileges
The user must be a member of the admin role. By default, the root user belongs to the admin role.
Syntax
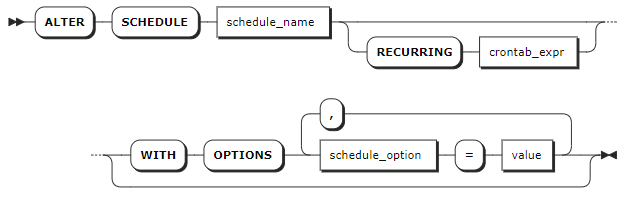
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
schedule_name | The name of the schedule to change. |
RECURRING crontab_expr | The recurring expression to execute a schedule. Available recurring expressions: - 7-field expression, also known as full-field expression: fields are separated using spaces ( <seconds> <minutes> <hours> <day-of-month> <month> <day-of-week> <year>), where the seconds field is pre-set to 0, indicating to execute the schedule for at 0 second. - 6-field expression: fields are separated using spaces ( <minutes> <hours> <day-of-month> <month> <day-of-week> <year>), where the year field is pre-set to *, indicating to execute the schedule for every year. - 5-field expression: fields are separated using spaces ( <minutes> <hours> <day-of-month> <month> <day-of-week>) - Pre-defined expressions include @annually (run a schedule once a year at midnight on the first day of January), @yearly (run a schedule once a year at midnight on the first day of January, same to @annually), @monthly (run a schedule once a month at midnight on the first day of the month ), @weekly (run a schedule once a week at midnight every Sunday), @daily (run a schedule once a day at midnight), @hourly (run hourly)For details about Crontab expression, see Crontab Expression. |
schedule_option | The options to execute a schedule. Available options: first_run: execute the schedule at the specified time. If not specified, execute the schedule based on the RECURRING expression by default. Support using TIMESTAMPTZ and NOW. on_execution_failure: if an error occurs during the schedule execution, do the following: - retry: retry the schedule right away. - pause: pause the schedule. This requires to manually resume the schedule. - reschedule: (Default) retry the schedule based on the RECURRING expression. on_previous_running: if the previous schedule is still running, do the following: - start: start the new schedule anyway, even if the previous one is still running. - skip: skip the new schedule. - wait: (Default) wait for the previous schedule to complete and then run the new schedule. |
Examples
This example changes the frequency to run the schedule.
ALTER SCHEDULE scheduled_table_statistics RECURRING '@hourly';
PAUSE SCHEDULE
When the system is performing high-load jobs such as importing a large amount of data, you can pause a pre-defined schedule to avoid further aggravating the system load or interfering with critical tasks. The PAUSE SCHEDULE command takes effect at the next scheduling time and does not affect the status of the currently running jobs or schedules.
The PAUSE SCHEDULE statement pauses a currently running schedule.
Privileges
The user must be a member of the admin role. By default, the root user belongs to the admin role.
Syntax
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
schedule_name | The name of the running schedule to pause. |
Examples
This example pauses a specified schedule.
PAUSE SCHEDULE scheduled_table_statistics;
RESUME SCHEDULE
The RESUME SCHEDULE statement resumes a paused schedule.
Privileges
The user must be a member of the admin role. By default, the root user belongs to the admin role.
Syntax
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
schedule_name | The name of the paused schedule to resume. |
Examples
This example resumes a specified schedule.
RESUME SCHEDULE scheduled_table_statistics;
DROP SCHEDULE
The DROP SCHEDULE statement removes a schedule. Currently, you can not remove scheduled_table_retention schedules that are automatically-created by the system.
Privileges
The user must be a member of the admin role. By default, the root user belongs to the admin role.
Syntax
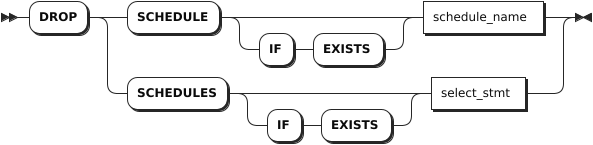
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
IF EXISTS | Optional. - When the IF EXISTS keyword is used, the system removes a schedule only if the target schedule has already existed. Otherwise, the system fails to remove the schedule without returning an error. - When the IF EXISTS keyword is not used, the system removes a schedule only if the target schedule has already existed. Otherwise, the system fails to remove the schedule and returns an error. |
schedule_name | The name of the schedule to remove. |
select_stmt | A selection query that returns names of schedules to remove. |
Examples
Remove a single schedule.
DROP SCHEDULE s1;Remove multiple schedules by nesting a
SELECTclause that retrieves name(s) inside theDROP SCHEDULESstatement.DROP SCHEDULES SELECT name FROM [SHOW SCHEDULES] WHERE schedule_status='PAUSED';