Time-Series Databases
As a multi-model database system, KWDB supports creating one or more database objects on a KWDB instance to manage time-series and relational data. One of the database objects dedicated to storing and managing time-series data is the time-series database. The time-series database includes the public schema and user-defined time-series tables.
CREATE DATABASE
The CREATE DATABASE statement creates a new time-series database.
Privileges
The user must be a member of the admin role. By default, the root user belongs to the admin role.
Syntax
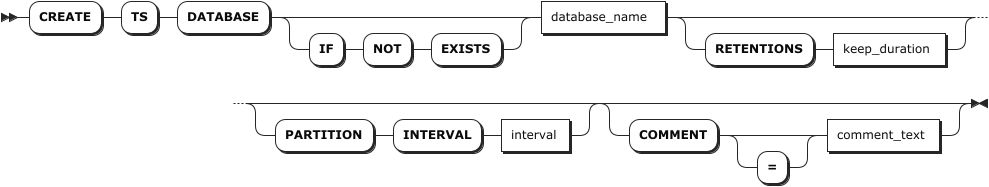
Parameters
Note
The optional parameters must be configured in an order of [RETENTIONS <keep_duration>] [PARTITION INTERVAL <interval>] [COMMENT [=] <'comment_text'>]. Otherwise, the system returns an error.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
IF NOT EXISTS | Optional. - When the IF NOT EXISTS keyword is used, the system creates a new database only if a database of the same name does not already exist. Otherwise, the system fails to create a new database without returning an error. - When the IF NOT EXISTS keyword is not used, the system creates a new database only if a database of the same name does not already exist. Otherwise, the system fails to create a new database and returns an error. |
database_name | The name of the database to create, which must be unique and follow these Identifier Rules. Currently, the name does not support Chinese characters and supports up to 63 bytes. |
keep_duration | Optional. Define the data retention period for the database. Data older than this duration will be automatically purged. Default: 0s (retain indefinitely)Time units: - Seconds: s or second- Minutes: m or minute- Hours: h or hour- Days: d or day- Weeks: w or week- Months: mon or month- Years: y or yearValid range: Positive integer up to 1000 years Note: - Table-level retention settings override database-level settings. - Longer retention periods consume more storage. Configure based on your business needs. - Data that already exceeds the retention period at write time will be rejected and not stored. |
interval | Optional. Specify the interval to partition the database. If not specified, it is set to 10d by default. Time units: - Days: d or day- Weeks: w or week- Months: mon or month- Years: y or yearValid range: Positive integer up to 1000 years |
comment_text | Optional. Specify the comment to be associated to the database. |
Examples
Create a database.
This example creates a database named
ts_db.CREATE TS DATABASE ts_db;If you succeed, you should see an output similar to the following:
CREATE TS DATABASECreate a database and set the retention of the database.
This example creates a database named
ts_db_tempand sets the database retention to50d.CREATE TS DATABASE ts_db_temp RETENTIONS 50d;If you succeed, you should see an output similar to the following:
CREATE TS DATABASECreate a database and specify comments for the database.
This example creates a database named
ts_db_powerand associates the comment textdatabase for power statisticsto the database.CREATE TS DATABASE ts_db_power COMMENT = 'database for power statistics';If you succeed, you should see an output similar to the following:
CREATE TS DATABASECreate a database and specify comments for the database.
This example creates a database named
ts_db_powerand associates the comment textdatabase for power statisticsto the database.CREATE TS DATABASE ts_db_power COMMENT = 'database for power statistics';If you succeed, you should see an output similar to the following:
CREATE TS DATABASECreate a database and specify an interval to partition the database.
This example creates a database named
iotand specifies the partition interval to2d.CREATE TS DATABASE iot PARTITION INTERVAL 2d;If you succeed, you should see an output similar to the following:
CREATE TS DATABASE
SHOW DATABASES
The SHOW DATABASES statement lists all databases in the KWDB cluster, including relational databases and time-series databases.
Privileges
N/A
Syntax
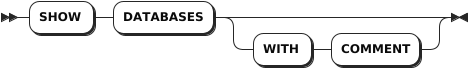
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
WITH COMMENT | Optional. Show a database's comments. By default, the database's comment is set to NULL. |
Examples
Note
The engine_type for time-series databases and relational databases is TIME SERIES and RELATIONAL respectively.
Show all created databases.
SHOW DATABASES;If you succeed, you should see an output similar to the following:
database_name | engine_type -----------------+------------------- defaultdb | RELATIONAL postgres | RELATIONAL system | RELATIONAL ts_db | TIME SERIES (4 rows)Show all created databases' comments.
SHOW DATABASES WITH COMMENT;If you succeed, you should see an output similar to the following:
database_name | engine_type | comment ----------------------+-------------+-------------------------------- defaultdb | RELATIONAL | NULL postgres | RELATIONAL | NULL ts_db | TIME SERIES | database for power statistics system | RELATIONAL | NULL (4 rows)
SHOW CREATE DATABASE
The SHOW CREATE DATABASE statement shows the SQL statement used to create a database, along with its configuration parameters.
For time-series databases, this command shows:
- The database name
- The
retentionsparameter value (displays the specified value, or0sif not explicitly set during creation)
Privileges
N/A
Syntax

Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
database_name | The name of the database to view. |
Examples
This example shows the statement that is used to create the tsdb1 database, and the values of related parameters.
-- 1. Create a database named tsdb1, and set retentions to `10d`.
CREATE TS DATABASE tsdb1 RETENTIONS 10d PARTITION INTERVAL 10d;
--2. Show the created tsdb1 database.
SHOW CREATE DATABASE tsdb1;
database_name | create_statement
----------------+-------------------------------
tsdb1 | CREATE TS DATABASE tsdb1
| retentions 864000s
| partition interval 10d
(1 row)
USE
The USE statement sets a target database to the current database.
Privileges
N/A
Syntax
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
db_name | The name of the database to use. |
Examples
This example sets the ts_db database to the current database.
USE ts_db;
ALTER DATABASE
The ALTER DATABASE statement applies a name, retention, or zone configurations to a database.
Privileges
Change the name of the database: the user must be a member of the
adminrole. By default, therootuser belongs to theadminrole.Change the retention of the database: the user must be a member of the
adminrole. By default, therootuser belongs to theadminrole.Change the zone configurations of the system database: the user must be a member of the
adminrole. By default, therootuser belongs to theadminrole.Modify zones for other databases: the user must be a member of the
adminrole or have been grantedCREATEorZONECONFIGprivileges. By default, therootuser belongs to theadminrole.
Syntax
Change the name of the database

Change the retention of the database

Change the zone configurations of the database
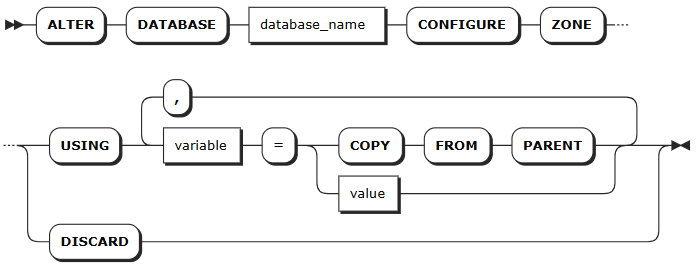
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
old_name | The name of the database to change. |
new_name | The new name of the database, which must be unique and follow these Identifier Rules. Currently, the name does not support Chinese characters and supports up to 63 bytes. |
database_name | The name of the database to change. |
keep_duration | Optional. Define the data retention period for the database. Data older than this duration will be automatically purged. Default: 0s (retain indefinitely)Time units: - Seconds: s or second- Minutes: m or minute- Hours: h or hour- Days: d or day- Weeks: w or week- Months: mon or month- Years: y or yearValid range: Positive integer up to 1000 years Note: - Table-level retention settings override database-level settings. - Longer retention periods consume more storage. Configure based on your business needs. - Data that already exceeds the retention period at write time will be rejected and not stored. |
variable | The name of the variable to modify. The following variables are supported: - range_min_bytes: the minimum size in bytes for a data range. When a range is smaller than this value, KWDB merges it with an adjacent range. Default: 256 MiB. The value must be greater than 1 MiB (1048576 bytes) and smaller than the maximum size of the range. - range_max_bytes: the maximum size in bytes for a data range. When a range exceeds this value, KWDB splits it into two ranges. Default: 512 MiB. The value must not be smaller than 5 MiB (5242880 bytes). - num_replicas: the number of replicas. Default: 3. For the system database and the meta, liveness, and system ranges, the default number of replicas is 5. Note: The number of replicas cannot be reduced when unavailable nodes exist in the cluster. - constraints: required (+) and/or prohibited (-) constraints for where replicas can be placed. For example, constraints = '{"+region=NODE1": 1, "+region=NODE2": 1, "+region=NODE3": 1}' places one replica on each of nodes 1, 2, and 3. Currently only supports the region=NODEx format. - lease_preferences: an ordered list of required (+) and/or prohibited (-) constraints for where the leaseholder should be placed. For example, lease_preferences = '[[+region=NODE1]]' prefers placing the leaseholder on node 1. If this isn't possible, KWDB tries the next preference in the list. If no preferences can be satisfied, KWDB uses the default lease distribution algorithm, which balances leases across nodes based on their current lease count. Each value in the list can contain multiple constraints. - ts_merge.days: the merging time for time-series data ranges. After ranges in the same time-series table at the same hash point are split by timestamp, ranges that exceed this time are automatically merged and won't be automatically split again. Default: 10 (10 days). The value must be greater than or equal to 0. When set to 0, time-series data ranges are automatically merged immediately after being split by timestamp. If network or other failures are caused by too many system ranges, you can reduce this value to mitigate data volume issues. Tips: - lease_preferences can be defined independently from the constraints field. - When setting constraints, you must also set num_replicas, and the number of constraints must be less than or equal to the number of replicas. The order of constraints doesn't matter. - By default, KWDB only splits ranges based on hash points, so the range merging by time is disabled by default. To support merging ranges by time, set the kv.kvserver.ts_split_interval runtime parameter to 1 and the kv.kvserver.ts_split_by_timestamp.enabled runtime parameter to true to enable splitting ranges by both hash points and timestamps. |
value | The value of the variable to change. |
COPY FROM PARENT | Use the settings of the parent zone. |
DISCARD | Remove the zone settings and use the default values. |
Examples
Change the name of a database.
This example renames the
ts_dbdatabase totsdb.ALTER DATABASE ts_db RENAME TO tsdb;Change the retention of a database.
This example sets the retention of the
tsdbdatabase to10 day.ALTER TS DATABASE tsdb SET RETENTIONS = 10 day;Change the zone configurations of a database.
This example sets the number of the replicas of the
tsdbdatabase to5.-- 1. Change the zone configurations of the tsdb database. ALTER DATABASE tsdb CONFIGURE ZONE USING num_replicas = 5; CONFIGURE ZONE 1 -- 2. Check whether the configurations are applied successfully. SHOW ZONE CONFIGURATION FOR DATABASE tsdb; target | config_sql ----------------+------------------------------------------- DATABASE tsdb | ALTER DATABASE tsdb CONFIGURE ZONE USING | range_min_bytes = 134217728, | range_max_bytes = 536870912, | gc.ttlseconds = 90000, | num_replicas = 5, | constraints = '[]', | lease_preferences = '[]' (1 row)
DROP DATABASE
The DROP DATABASE statement removes a database and all its objects from a KWDB cluster. To remove the current database, use the USE <database_name> statement to set another database as the current database. After deletion, all privileges on the database and its tables are also removed.
Note
When removing a database, KWDB will check whether the current database is referenced by the stream computing service. If yes, the system ruturns an error and lists all streams that reference the specified database. In this case, you can use the CASCADE keyword to remove the specified database and its dependent objects.
Privileges
The user must be a member of the admin role or have the DROP privilege on the specified database and tables in the database. By default, the root user belongs to the admin role.
Syntax
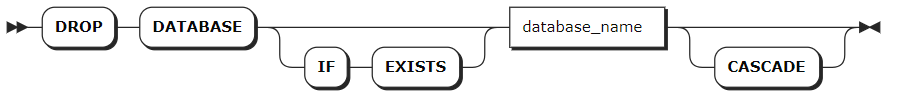
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
IF EXISTS | Optional. - When the IF EXISTS keyword is used, the system removes the database only if the database has already existed. Otherwise, the system fails to remove the database without returning an error. - When the IF EXISTS keyword is not used, the system removes the database only if the database has already existed. Otherwise, the system fails to remove the database and returns an error. |
database_name | The name of the database to remove. |
CASCADE | Optional. Remove all tables in the database. The CASCADE keyword does not list objects it removes, so it should be used cautiously. |
Examples
This example removes the tsdb database and its dependent objects using the CASCADE keyword.
-- 1. Show tables in the tsdb database.
SHOW TABLES FROM tsdb;
table_name | table_type
--------------+--------------------
sensor_data | TIME SERIES TABLE
temp | TIME SERIES TABLE
water | TIME SERIES TABLE
(3 rows)
-- 2. Remove the tsdb database and its dependent objects.
DROP DATABASE tsdb CASCADE;
DROP DATABASE
-- 3. Show tables in the tsdb database.
SHOW TABLES FROM tsdb;
ERROR: target database or schema does not exist