Partitions
Table partitioning is a database optimization technique that distributes table data across specified nodes based on defined rules. This provides row-level control over data storage locations, reducing query latency and improving overall performance.
How It Works
Table partitioning in KWDB relies on two core components working together:
Partition Definition
When altering a table, you can set hashpoint partitioning. The system automatically assigns data to different partitions based on hash values. KWDB supports the following two partitioning methods:
- Partitioning by specified values: Assigns specific hash values to partitions (e.g., assigning hash values 1 and 5 to partition A)
- Partitioning by continuous range: Assigns hash value ranges to partitions (e.g., assigning hash values 1-100 to partition B)
Partition configuration is tightly bound to the table's lifecycle. When a table is deleted, the partition configuration automatically becomes invalid. When resetting table partitions, the new configuration overwrites the original settings, and the system automatically cleans up zone configuration information for deleted partitions.
Partition configuration operations support repeated execution, making it convenient to adjust partitioning strategies as needed.
For best results, align your partition settings with your range distribution. This ensures ranges are distributed to the intended target nodes. Note: Partition settings don't re-split existing ranges. Instead, they control where data replicas are stored, which optimizes performance by placing data closer to where it's accessed.
Zone Configuration
Partition definitions only add identifiers to table rows that meet specified conditions. To make partitions truly effective, zones need to be configured and applied to the corresponding partitions.
Configuration priority: partition > table > database
Create Partition
Privileges
The user must be a member of the admin role or have CREATE privileges on the target table. The root user belongs to the admin role by default.
Syntax
Note
The following syntax shows only the parameters required for creating partitions. For all parameters supported for altering tables, see Alter Table.
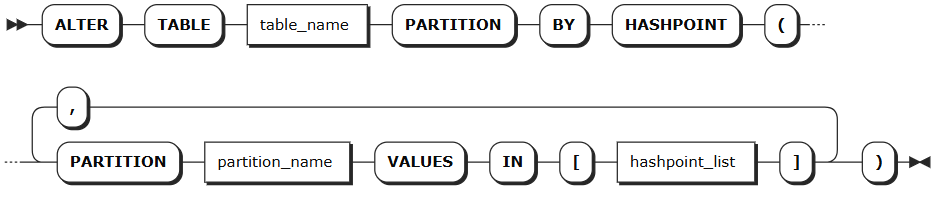
Partitioning by specified values:
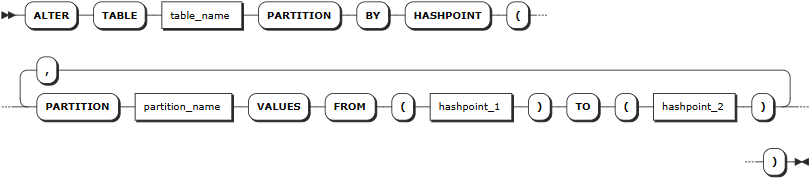
Partitioning by continuous ranges:
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
table_name | The name of the table containing the partition |
partition_name | Partition name |
hashpoint_list | List of hash values, separated by commas, e.g., 1,3,5,7 |
hashpoint_1 | Starting hash value for range partition (inclusive), must be an integer |
hashpoint_2 | Ending hash value for range partition (exclusive), must be an integer |
Examples
Partitioning by specified hash values
-- Create partitions by specified hash values ALTER TABLE orders PARTITION BY HASHPOINT ( PARTITION p_region_1 VALUES IN [1, 3, 5, 7], PARTITION p_region_2 VALUES IN [2, 4, 6, 8], PARTITION p_region_3 VALUES IN [9, 10] );Partitioning by specified hash value ranges
-- Create partitions by hash value ranges ALTER TABLE users PARTITION BY HASHPOINT ( PARTITION p_low VALUES FROM (0) TO (100), PARTITION p_medium VALUES FROM (100) TO (200), PARTITION p_high VALUES FROM (200) TO (300) );
Alter Partition
The ALTER PARTITION statement is used to modify the replica zone configuration of table partitions.
Note
- Node health and scale-in impact: Your configured
lease_preferencesandconstraintsmay not apply as expected if target nodes are unhealthy or is undergoing scale-in operations. - High availability and scale-in behavior:
- When a node fails,
lease_preferencespointing to that node will stop working, but the system maintains high availability. Note thatconstraintssettings may prevent the system from replenishing replicas. - During scale-in operations,
lease_preferencesmay stop working while high availability is maintained. However,constraintssettings may block the scale-in operation from completing.
- When a node fails,
Privileges
The user must be a member of the admin role or have CREATE privileges on the target table. By default, the root user is a member of the admin role.
Syntax
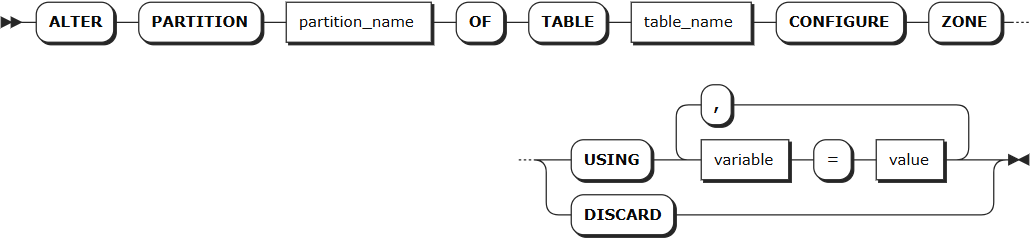
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
partition_name | The name of the partition to be modified |
table_name | The name of the table containing the partition |
variable | Supports modifying the following variables: - num_replicas: Number of replicas. Default is 3- constraints: Required (+) and/or prohibited (-) constraints for where replicas can be placed. For example, constraints = '{"+region=NODE1": 1, "+region=NODE2": 1, "+region=NODE3": 1}' places one replica on each of node 1, node 2, and node 3. Currently only supports the region=NODEx format- lease_preferences: An ordered list of required (+) and/or prohibited (-) constraints for where the leaseholder should be placed. For example, lease_preferences = '[[+region=NODE1]]' prefers placing the leaseholder on node 1. If this isn't possible, KWDB tries the next preference in the list. If no preferences can be satisfied, KWDB uses the default lease distribution algorithm, which balances leases across nodes based on their current lease count. Each value in the list can contain multiple constraintsNote: - Lease preferences can be defined independently from the constraints field- When setting constraints, you must also set num_replicas, and the number of constraints must be less than or equal to num_replicas. The order of constraints doesn't matter |
value | Variable value, which can be a specific value or COPY FROM PARENT, indicating to use the parent zone's setting value |
DISCARD | Remove zone configuration and adopt default values |
Examples
-- Low hash value partition: Data stored on all nodes, leaseholder prefers node 1
ALTER PARTITION p_low OF TABLE users
CONFIGURE ZONE USING
num_replicas = 3,
constraints = '{"+region=NODE1": 1, "+region=NODE2": 1, "+region=NODE3": 1}',
lease_preferences = '[[+region=NODE1]]';
-- Medium hash value partition: Data stored on all nodes, leaseholder prefers node 2
ALTER PARTITION p_medium OF TABLE users
CONFIGURE ZONE USING
num_replicas = 3,
constraints = '{"+region=NODE1": 1, "+region=NODE2": 1, "+region=NODE3": 1}',
lease_preferences = '[[+region=NODE2]]';
-- High hash value partition: Data stored on all nodes, leaseholder prefers node 3
ALTER PARTITION p_high OF TABLE users
CONFIGURE ZONE USING
num_replicas = 3,
constraints = '{"+region=NODE1": 1, "+region=NODE2": 1, "+region=NODE3": 1}',
lease_preferences = '[[+region=NODE3]]';
-- Insert test data
INSERT INTO users (created_at, id, name, email, region) VALUES
('2024-01-15 09:30:00', 1, 'Zhang Wei', 'zhangwei@example.com', 'North'),
('2024-01-15 10:15:30', 2, 'Li Ming', 'liming@example.com', 'East'),
('2024-01-15 11:20:45', 3, 'Wang Lei', 'wanglei@example.com', 'South'),
('2024-02-10 14:25:12', 101, 'Liu Fang', 'liufang@example.com', 'West'),
('2024-02-10 15:40:28', 102, 'Chen Xin', 'chenxin@example.com', 'North'),
('2024-03-05 08:55:33', 201, 'Yang Hao', 'yanghao@example.com', 'East'),
('2024-03-05 16:10:18', 202, 'Zhou Mei', 'zhoumei@example.com', 'South');
-- View data distribution
SELECT database_name, table_name, range_id, start_pretty, end_pretty, lease_holder, replicas, range_size
FROM kwdb_internal.ranges
WHERE database_name = 'ecommerce_orders' AND table_name = 'users';