Privilege Management
KWDB supports managing privileges on objects within a database to ensure database security. This table lists all privileges supported by KWDB.
| Privilege | Object | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | - DATABASE - TABLE - SCHEMA (only available for relational databases) | Perform all operations on the specified object(s). |
| CREATE | - DATABASE - TABLE - SCHEMA (only available for relational databases) | Create one or more objects. |
| DROP | - DATABASE - TABLE - SCHEMA (only available for relational databases) | Remove the specified object(s). |
| GRANT | - DATABASE - TABLE - SCHEMA (only available for relational databases) | Grant privileges to the specific user(s). |
| SELECT | TABLE | Query data from the specified table(s). |
| INSERT | TABLE | Insert data into the specified table(s). |
| DELETE | TABLE | Remove data from the specified table(s). |
| UPDATE | TABLE | Update the specified table(s). |
GRANT {privileges}
The GRANT <privileges> statement grants privileges on the specified objects to one or more users/roles.
Note
If the privileges of a user are not updated on time, you can remove the user and then create a new user with a different name and re-grant privileges to the new user.
Privileges
The user granting the privileges must also have the GRANT privilege on the specified database(s), table(s) or schema(s) (only for user-defined schema of relational databases). For example, a user granting the SELECT privilege on a table to another user must have the GRANT and SELECT privileges on that table.
Syntax
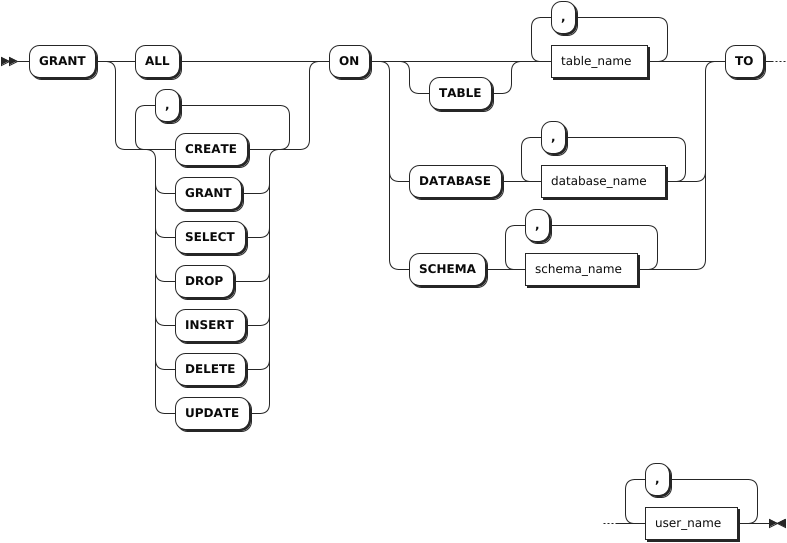
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
table_name | A comma-separated list of table names to grant privileges on. |
database_name | A comma-separated list of database names to grant privileges on. |
schema_name | A comma-separated list of schema names to grant privileges on. Note This parameter is available only for the relationdal database. |
user_name | A comma-separated list of role or user names to grant privileges to. |
Examples
This example grants the CREATE privilege to create the db1 and defaultdb databases to operatora user.
GRANT CREATE ON DATABASE db1, defaultdb TO operatora;
REVOKE {Privileges}
The REVOKE <privileges> statement revokes privileges on the specified objects from one or more users/roles.
Privileges
The user revoking the privileges must also have the GRANT privilege on the specified database(s), table(s) or schema(s) (only for user-defined schema of relational databases). For example, a user revoking the SELECT privilege on a table from another user must have the GRANT and SELECT privileges on that table.
Syntax
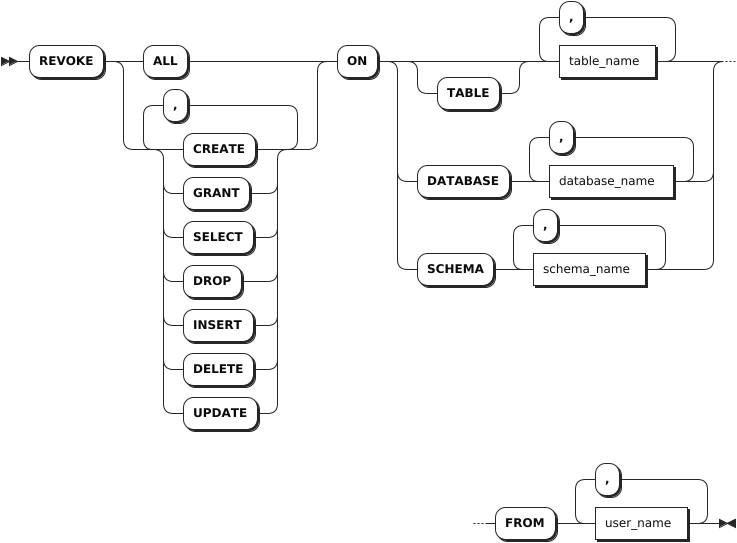
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
table_name | A comma-separated list of table names to revoke privileges from. |
database_name | A comma-separated list of database names to revoke privileges from. |
schema_name | A comma-separated list of schema names to revoke privileges from. Note This parameter is available only for the relationdal database. |
user_name | A comma-separated list of role or user names to revoke privileges from. |
Examples
This example revokes the CREATE privilege to create the db1 and defaultdb databases from user11 user.
REVOKE CREATE ON DATABASE db1, defaultdb FROM user11;
SHOW GRANTS
The SHOW GRANTS statement lists one of the following:
- The roles granted to users in a cluster.
- The privileges granted to users on databases, tables, or user-defined schemas (only for user-defined schema of relational databases).
Privileges
N/A. To run the SHOW GRANTS ON ROLE command, the user must have been granted the SELECT privilege on the system table.
Syntax
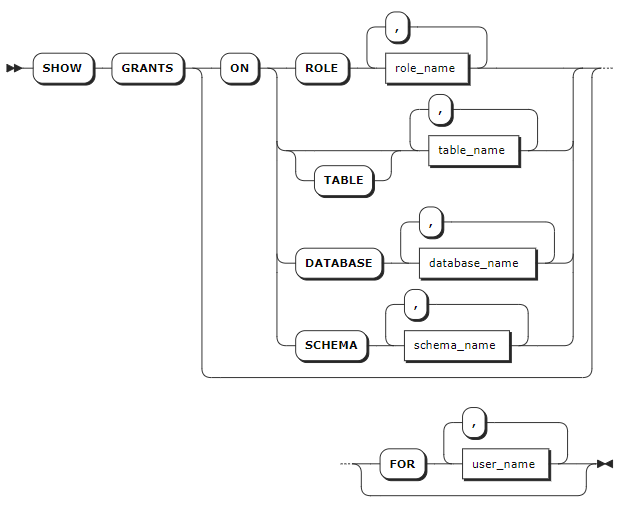
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
table_name | A comma-separated list of table names to check privileges on. |
database_name | A comma-separated list of database names to check privileges on. |
schema_name | A comma-separated list of schema names to check privileges on. Note This parameter is available only for the relationdal database. |
user_name | A comma-separated list of roles or users whose grants to show. |
Examples
This example shows grants on the defaultdb.t1 table.
SHOW GRANTS ON TABLE defaultdb.t1;
If you succeed, you should see an output similar to the following:
database_name|schema_name|table_name|grantee|privilege_type
-------------+-----------+----------+-------+--------------
defaultdb |public |t1 |admin |ALL
defaultdb |public |t1 |root |ALL
defaultdb |public |t1 |user11 |DELETE
(3 rows)