Jobs
SHOW JOBS
The SHOW JOBS statement lists all long-running tasks your cluster has performed in the last 12 hours, including:
- Schema changes triggered by
ALTER TABLE,DROP DATABASE, andDROP TABLEstatements - Import and export jobs
- Historical restart jobs
- Stream computing jobs
- User-created table statistics jobs for use by the cost-based optimizer. Automatic table statistics jobs are not included in
SHOW JOBSresults. To view automatic table statistics jobs, use theSHOW AUTOMATIC JOBSstatement.
KWDB first checks all running jobs, then checks jobs completed in the last 12 hours. Running jobs are sorted by start time, while completed jobs are sorted by end time.
Note
- The
SHOW JOBSstatement is only used to view long-running jobs. To view all running jobs, use SQL audit logs (experimental). - To view details for jobs older than 12 hours, query the
kwdb_internal.jobstable. - By default, the system retains job records for 14 days. You can configure the retention period using the
jobs.retention_timecluster setting.
Privileges
The user must be a member of the admin role. By default, the root user belongs to the admin role.
Syntax
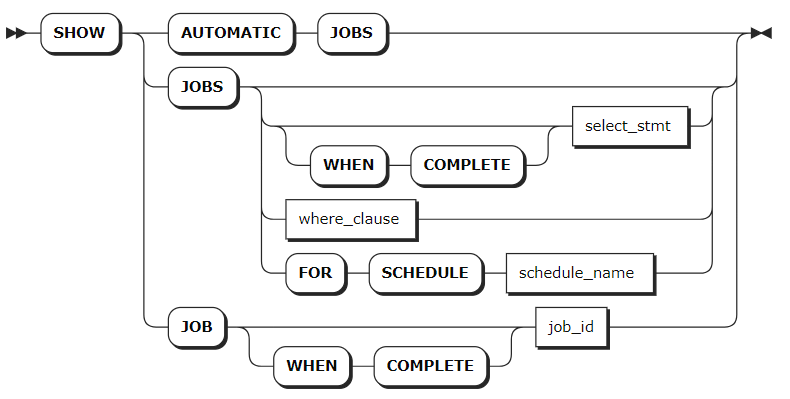
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
SHOW AUTOMATIC JOBS | View jobs required for internal operations. |
select_stmt | A selection query that returns the IDs of jobs to view. |
where_clause | A WHERE clause to filter qualified jobs from historical records. |
WHEN COMPLETE | Block the SHOW JOBS or SHOW JOB statement until the specified job reaches a terminal state. |
schedule_name | The name of the schedule to view. For more information, see Schedules. |
job_id | The ID of the job to view. |
Response Fields
The following table lists the fields returned for each job.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
job_id | A unique ID identifying each job. This value is used for pausing, resuming, or canceling jobs. |
job_type | The type of job, including: - UNSPECIFIED (unspecified jobs) - CHANGEFEED (change feed jobs) - IMPORT (import jobs) - EXPORT (export jobs) - SCHEMA CHANGE (schema change jobs) - SCHEMA CHANGE GC (schema change GC jobs) - CREATE_STATS (user-created table statistics jobs) - AUTO_CREATE_STATS (automatic table statistics jobs) - REPLICATION_STREAM (stream computing replication jobs) - REPLICATION_INGESTION (data ingestion replication jobs) - RESTART (historical restart jobs) - SYNC_META_CACHE (metadata cache synchronization jobs) - STREAM (stream computing jobs) - SUBSCRIPTION (data subscription jobs) |
description | The statement that started the job, or a textual description of the job. |
statement | When the description field contains a textual description, this field returns the statement that started the job. Currently, this field is only available for automatic table statistics jobs. |
user_name | The name of the user who started the job. |
status | The job's current state. Available values: - pending: The job is created but has not started executing. - running: The job is executing. For multi-execution jobs, this indicates the overall task is executing. - failed: The job failed to execute. For multi-execution jobs, this indicates a single execution has failed. - succeeded: The job completed successfully and will not run again. - canceled: The job was canceled. - reverting: The job failed or was canceled and its changes are being reverted. - revert-failed: The job encountered a non-retryable error when reverting changes. Manual cleanup is required for jobs with this status. |
running_status | The job's detailed running status. KWDB provides progress visualization for DROP and TRUNCATE table operations. The running status of DROP or TRUNCATE operations depends on the table's initial schema change. After the GC TTL expires, the job completes and the table data and ID are deleted. When executing the SHOW AUTOMATIC JOBS statement, this field returns NULL. |
created | The timestamp when the job was created. |
started | The timestamp when the job started running. |
finished | The timestamp when the job reached succeeded, failed, or canceled state. |
modified | The timestamp when the job was last modified. |
errord | The timestamp when the job encountered an error. |
fraction_completed | The fraction of the job that has been completed, with values between 0.00 and 1.00. |
error | The error message when the job is in failed state. |
coordinator_id | The ID of the node running the job. |
total_num_of_ex | The total number of executions for a multi-execution job. |
total_num_of_success | The total number of successful executions for a multi-execution job. |
total_num_of_fail | The total number of failed executions for a multi-execution job. |
time_of_last_success | The timestamp of the last successful execution for a multi-execution job. |
Examples
View all jobs.
show jobs;If you succeed, you should see an output similar to the following:
job_id | job_type | description | statement | user_name | status | running_status | created | started | finished | modified | errord | fraction_completed | error | coordinator_id | total_num_of_ex | total_num_of_success | total_num_of_fail | time_of_last_success ---------------------+---------------+--------------------+-----------+-----------+-----------+----------------+----------------------------------+----------------------------------+----------------------------------+---------------------------------+--------+--------------------+-------+----------------+-----------------+----------------------+-------------------+----------------------------------- 966387435059478529 | SCHEMA CHANGE | DROP DATABASE jobs | | root | succeeded | NULL | 2024-05-06 09:40:40.481926+00:00 | 2024-05-06 09:40:40.511037+00:00 | 2024-05-06 09:40:40.518282+00:00 | 2024-05-06 09:40:40.51671+00:00 | NULL | 1 | | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2024-05-06 09:40:40.518282+00:00 (1 row)Filter jobs using the
SELECTandWHEREstatements.SELECT * FROM [SHOW JOBS] WHERE job_type = 'SCHEMA CHANGE';If you succeed, you should see an output similar to the following:
job_id |job_type |description |statement|user_name|status |running_status|created |started |finished |modified |fraction_completed|error|coordinator_id| error_time ------------------|-------------|--------------------------------------------------------------------------|---------|---------|---------|--------------|-----------------------|-----------------------|-----------------------|-----------------------|------------------|-----|--------------|----------- 902041667031498753|SCHEMA CHANGE|DROP DATABASE iot_db | |kaiwudb |succeeded| |2023-09-22 03:01:10.452|2023-09-22 03:01:10.797|2023-09-22 03:01:11.249|2023-09-22 03:01:11.248| 1| | 1| (1 row)Filter historical jobs using the
WHEREclause.show jobs where job_type = 'SCHEMA CHANGE';If you succeed, you should see an output similar to the following:
job_id | job_type | description | statement | user_name | status | running_status | created | started | finished | modified | errord | fraction_completed | error | coordinator_id | total_num_of_ex | total_num_of_success | total_num_of_fail | time_of_last_success ---------------------+---------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+-----------+-----------+-----------+----------------+----------------------------------+----------------------------------+----------------------------------+----------------------------------+--------+--------------------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+----------------+-----------------+----------------------+-------------------+----------------------------------- 962704207243051009 | SCHEMA CHANGE | CREATE TABLE db2.public.orders (customer INT4, id INT4, total DECIMAL(20,5), PRIMARY KEY (customer, id), CONSTRAINT fk_customer FOREIGN KEY (customer) REFERENCES db2.public.customers) INTERLEAVE IN PARENT db2.public.customers (customer) | | root | succeeded | NULL | 2024-04-23 09:26:48.552734+00:00 | 2024-04-23 09:26:48.603675+00:00 | 2024-04-23 09:26:48.616608+00:00 | 2024-04-23 09:26:48.614163+00:00 | NULL | 1 | | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2024-04-23 09:26:48.616608+00:00 962704207250391041 | SCHEMA CHANGE | updating referenced table;updating ancestor table | | root | succeeded | NULL | 2024-04-23 09:26:48.552734+00:00 | 2024-04-23 09:26:48.597467+00:00 | 2024-04-23 09:26:48.60655+00:00 | 2024-04-23 09:26:48.605119+00:00 | NULL | 1 | | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2024-04-23 09:26:48.60655+00:00 962704243914113025 | SCHEMA CHANGE | CREATE TABLE db2.public.packages (customer INT4, "order" INT4, id INT4, address STRING(50), delivered BOOL, delivery_date DATE, PRIMARY KEY (customer, "order", id), CONSTRAINT fk_order FOREIGN KEY (customer, "order") REFERENCES db2.public.orders) INTERLEAVE IN PARENT db2.public.orders (customer, "order") | | root | succeeded | NULL | 2024-04-23 09:26:59.743004+00:00 | 2024-04-23 09:26:59.799601+00:00 | 2024-04-23 09:26:59.810892+00:00 | 2024-04-23 09:26:59.809259+00:00 | NULL | 1 | | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2024-04-23 09:26:59.810892+00:00 962704243924926465 | SCHEMA CHANGE | updating referenced table;updating ancestor table | | root | succeeded | NULL | 2024-04-23 09:26:59.743004+00:00 | 2024-04-23 09:26:59.791893+00:00 | 2024-04-23 09:26:59.806047+00:00 | 2024-04-23 09:26:59.803297+00:00 | NULL | 1 | | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2024-04-23 09:26:59.806047+00:00 962907066109952001 | SCHEMA CHANGE | DROP TABLE db2.public.example_table, db2.public.testblob | | root | succeeded | NULL | 2024-04-24 02:38:36.156104+00:00 | 2024-04-24 02:38:36.210874+00:00 | 2024-04-24 02:38:36.24302+00:00 | 2024-04-24 02:38:36.240734+00:00 | NULL | 1 | | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2024-04-24 02:38:36.24302+00:00View automatic jobs.
SHOW AUTOMATIC JOBS;If you succeed, you should see an output similar to the following:
job_id |job_type |description |statement |user_name|status |running_status|created |started |finished |modified |fraction_completed|error|coordinator_id| error_time ------------------|-----------------|--------------------------------------------------------|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|---------|---------|--------------|-----------------------|-----------------------|-----------------------|-----------------------|------------------|-----|--------------|----------- 902025989139169281|AUTO CREATE STATS|Table statistics refresh for defaultdb."1".newtable |CREATE STATISTICS __auto__ FROM [15093] WITH OPTIONS THROTTLING 0.9 AS OF SYSTEM TIME '-10s'|kaiwudb |succeeded| |2023-09-22 01:41:25.943|2023-09-22 01:41:25.950|2023-09-22 01:41:25.988|2023-09-22 01:41:25.986| 1| | 1| 902024809042214913|AUTO CREATE STATS|Table statistics refresh for defaultdb."1".newtable |CREATE STATISTICS __auto__ FROM [15093] WITH OPTIONS THROTTLING 0.9 AS OF SYSTEM TIME '-10s'|kaiwudb |succeeded| |2023-09-22 01:35:25.806|2023-09-22 01:35:25.901|2023-09-22 01:35:25.932|2023-09-22 01:35:25.931| 1| | 1| (2 rows)
Pause Jobs
The PAUSE JOB statement pauses import and export jobs, full backup and restore jobs, user-created table statistics jobs, and automatic table statistics jobs. After pausing jobs, you can resume them with the RESUME JOB statement.
Note
- You cannot pause schema change jobs.
- To disable automatic table statistics jobs, set the
sql.stats.automatic_collection.enabledcluster setting tofalse.
Privileges
The user must be a member of the admin role. By default, the root user belongs to the admin role.
Syntax
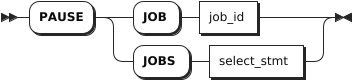
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
job_id | The ID of the job to pause, which can be found with the SHOW JOBS statement. |
select_stmt | A selection query that returns the IDs of jobs to pause. |
Examples
Pause a single job.
PAUSE JOB 505396193949089793;Use the
SELECTclause to query job IDs and pause multiple jobs.PAUSE JOBS (SELECT job_id FROM [SHOW JOBS] WHERE user_name = 'stone');
Resume Jobs
The RESUME JOB statement resumes paused jobs.
Privileges
The user must be a member of the admin role. By default, the root user belongs to the admin role.
Syntax
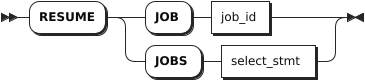
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
job_id | The ID of the job to resume, which can be found with the SHOW JOBS statement. |
select_stmt | A selection query that returns the IDs of jobs to resume. |
Examples
Resume a single job.
RESUME JOB 27536791415282;Use the
SELECTclause to query job IDs and resume multiple jobs.RESUME JOBS (SELECT job_id FROM [SHOW JOBS] WHERE user_name = 'stone');
CANCEL JOB
The CANCEL JOB statement stops long-running jobs, including schema change jobs, backup and restore jobs, user-created table statistics jobs, and automatic table statistics jobs.
Note
After canceling an automatic table statistics job, the system will automatically restart the job immediately. To disable automatic table statistics jobs, set the sql.stats.automatic_collection.enabled cluster setting to false.
Privileges
The user must be a member of the admin role. By default, the root user belongs to the admin role.
Syntax
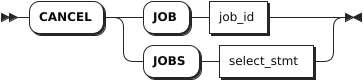
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
job_id | The ID of the job to cancel, which can be found with the SHOW JOBS statement. |
select_stmt | A selection query that returns the IDs of jobs to cancel. |
Examples
Cancel a single job.
CANCEL JOB 27536791415282;Use the
SELECTclause to query job IDs and cancel multiple jobs.CANCEL JOBS (SELECT job_id FROM [SHOW JOBS] WHERE user_name = 'stone');