Time-Series Tables
The time-series table stores time-series data.
CREATE TABLE
The CREATE TABLE statement creates a new table in a database.
Privileges
The user must be a member of the admin role or have been granted the CREATE privilege on the specified database(s). By default, the root user belongs to the admin role.
Syntax
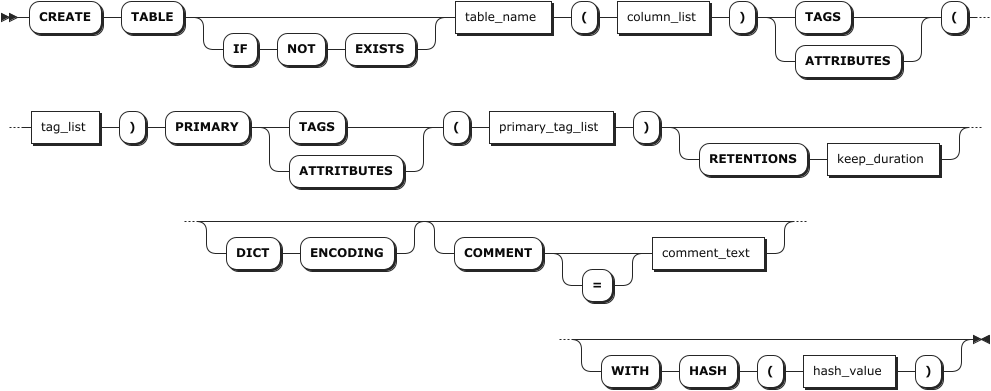
Parameters
Note
- Currently, the table name, column name, and tag name do not support Chinese characters.
- The optional parameters must be configured in an order of
[RETENTIONS <keep_duration>] [DICT ENCODING] [COMMENT [=] <'comment_text'>]. Otherwise, the system returns an error. - For KWDB 3.1.0, the partition interval configuration of a table is inherited from that of its parent database.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
IF NOT EXISTS | Optional. - When the IF NOT EXISTS keyword is used, the system creates a new table only if a table of the same name does not already exist. Otherwise, the system fails to create a new table without returning an error. - When the IF NOT EXISTS keyword is not used, the system creates a new table only if a table of the same name does not already exist. Otherwise, the system fails to create a new table and returns an error.Note IF NOT EXISTS checks the table name only. It does not check if an existing table has the same columns, indexes, constraints, etc., of the new table. |
table_name | The name of the table to create, which must be unique within its database and follow these Identifier Rules. The table name supports up to 128 bytes. |
column_list | A comma-separated list of columns. You can specify two or more columns. Each column requires a name, data type, and default value. Each table supports up to 4096 columns. The column name supports up to 128 bytes. You can set the data type to NOT NULL. By default, the data type is set to NULL. For non-TIMESTAMP data columns, the default value must be a constant. For TIMESTAMP-typed columns, the default value can either be a constant or the now() function. If the data type of the default value is not matched with that of the column, the system returns an error. KWDB supports setting NULL as the default value. Support adding comments to data columns after the data type. |
tag_list | A comma-separated list of tags. You can specify one or more tags. Each table supports up to 128 tags. Each tag requires a name and data type. The tag name supports up to 128 bytes. You can set the data type to NOT NULL. By default, the data type is set to NULL. KWDB does not support setting TIMESTAMP, TIMESTAMPTZ, NVARCHAR or GEOMETRY data types for time-series tables. Support adding comments to tag columns after the nullable condition. |
primary_tag_list | A comma-separated list of primary tags. You can specify one or more primary tags. Each table supports up to 4 primary tags. Primary tags must be included in the list of tags and set to NOT NULL. Currently, primary tags does not support floating-point and variable-length data types, except for the VARCHAR data type. By default, a VARCHAR-typed data length is 64 bytes. The maximum of a VARCHAR-typed data length is 128 bytes. |
keep_duration | Optional. Define the data retention period for the database. Data older than this duration will be automatically purged. Default: 0s (retain indefinitely)Time units: - Seconds: s or second- Minutes: m or minute- Hours: h or hour- Days: d or day- Weeks: w or week- Months: mon or month- Years: y or yearValid range: Positive integer up to 1000 years Note: - Table-level retention settings override database-level settings. - Longer retention periods consume more storage. Configure based on your business needs. - Data that already exceeds the retention period at write time will be rejected and not stored. |
DICT ENCODING | Optional. Enable dictionary encoding to improve the compression capability of STRING-typed data. The higher the repetition rate of the STRING-typed data is, the better the data is compressed. This function is only applied to CHAR- and VARCHAR-typed data whose length is less than or equal to 1023. You can only enable it when creating a table. Once enabled, you cannot disable it. |
comment_text | Optional. Specify the comment to be associated to the table. |
hash_value | Optional. Define the HASH ring size in a distributed cluster, which determines the maximum number of data ranges. For example, HASH(100) allows up to 100 distinct ranges.Default: 2000 (up to 2000 ranges) Valid range: [1, 50000] Performance considerations: - Too small: Data from multiple devices concentrates in fewer ranges, causing write hotspots - Too large: Excessive ranges increase management overhead Recommended values based on device count: - ≤ 1,000 devices: hash_value < 20- ≤ 50,000 devices: hash_value < 2,000- ≤ 1,000,000 devices: hash_value < 10,000 |
Examples
Create a table.
-- 1. Create a table named sensor_data. CREATE TABLE sensor_data ( k_timestamp TIMESTAMP NOT NULL, temperature FLOAT NOT NULL, humidity FLOAT, pressure FLOAT ) TAGS ( sensor_id INT NOT NULL, sensor_type VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL ) PRIMARY TAGS (sensor_id); -- 2. Check the created table. SHOW CREATE sensor_data; table_name | create_statement --------------+----------------------------------------------------------------- sensor_data | CREATE TABLE sensor_data ( | k_timestamp TIMESTAMPTZ(3) NOT NULL, | temperature FLOAT8 NOT NULL, | humidity FLOAT8 NULL, | pressure FLOAT8 NULL | ) TAGS ( | sensor_id INT4 NOT NULL, | sensor_type VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL ) PRIMARY TAGS(sensor_id) | retentions 864000s | activetime 1d (1 row)Create a table and set the retention for the table.
-- 1. Create a table named temp and set the retention to 20D. CREATE TABLE temp (ts TIMESTAMP NOT NULL, value FLOAT) TAGS (sensor_id INT NOT NULL) PRIMARY TAGS (sensor_id) RETENTIONS 20D; CREATE TABLE -- 2. Check the retention of the table. SHOW RETENTIONS ON TABLE temp; name | retentions | sample -------+------------+--------- temp | 20d | NULL (1 row)Create a table and enable dictionary encoding.
CREATE TABLE water (ts TIMESTAMP NOT NULL, value FLOAT) TAGS (sensor_id INT NOT NULL) PRIMARY TAGS (sensor_id) DICT ENCODING;Create a table and associate comments to the data columns, the tag columns and the table.
This example creates a table named
device_infoand associates comments to the data columns, the tag columns and the table.CREATE TABLE device_info (create_time TIMESTAMPTZ NOT NULL, device_id INT COMMENT 'device ID' NOT NULL, install_date TIMESTAMPTZ, warranty_period INT2) TAGS (plant_code INT2 NOT NULL COMMENT = 'plant code', workshop VARCHAR(128) NOT NULL, device_type CHAR(1023) NOT NULL, manufacturer NCHAR(254) NOT NULL) PRIMARY TAGS(plant_code, workshop, device_type, manufacturer) COMMENT = 'table for device information';Create a time-series table with a custom HASH ring size.
This example creates a time-series table named
sensorswith a HASH ring size of 20.CREATE TABLE sensors (ts TIMESTAMP NOT NULL, value FLOAT) TAGS (sensor_id INT NOT NULL) PRIMARY TAGS (sensor_id) WITH HASH(20);
SHOW TABLES
The SHOW TABLES statement lists the tables in a database.
Privileges
The user must have any privilege on the specified table(s).
Syntax
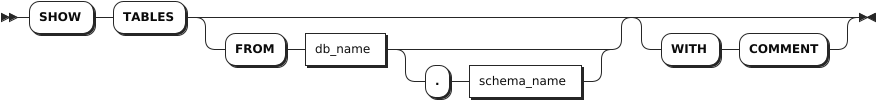
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
db_name | The name of the database for which to show tables. If not specified, use the current database. |
schema_name | Optional. The name of the schema for which to show tables. Currently, only the public schema is supported. |
table_name | The name of the table to show. |
WITH COMMENT | Optional. Show a table's comments. By default, the table's comment is set to NULL. |
Examples
Show all the tables in the current database.
SHOW TABLES;If you succeed, you should see an output similar to the following:
table_name | table_type --------------+------------------------------- sensor_data | TIME SERIES TABLEShow tables in a specified database.
SHOW TABLES FROM tsdb;If you succeed, you should see an output similar to the following:
table_name | table_type --------------+-------------------- t1 | TIME SERIES TABLE t2 | TIME SERIES TABLE t3 | TIME SERIES TABLE t4 | TIME SERIES TABLE t5 | TIME SERIES TABLE (5 rows)Show a table's comment.
-- 1. Add a comment for the power table. COMMENT ON TABLE power IS 'power for all devices'; COMMENT ON TABLE -- 2. Check comments of the power table. SHOW TABLES WITH COMMENT; table_name | table_type | comment --------------+-------------------+-------------------- power | TIME SERIES TABLE | power for all devices (1 row)
SHOW CREATE TABLE
The SHOW CREATE [TABLE] <table_name> statement displays shows the SQL statement used to create a table, along with its configuration parameters. If no database is specified, the current database is used.
For time-series tables, the output includes:
- The table name
- The
retentionsparameter value (displays the specified value, or0sif not explicitly set during creation)
Privileges
The user must have any privilege on the specified table(s).
Syntax
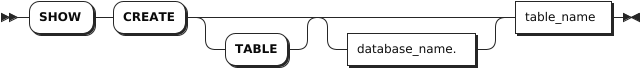
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
database_name | The name of the database for which to show created tables. If not specified, use the current database. |
table_name | The name of the table to show. |
Examples
Show the
CREATE TABLEstatement for a table in the current database.-- 1. Create a table named t3 and set a value for the activetime parameter. CREATE TABLE t3(ts timestamp NOT NULL, a int) TAGS(ptag int NOT NULL) PRIMARY TAGS(ptag) ACTIVETIME 10s; -- 2. Checkt the created t3 table. SHOW CREATE TABLE t3; table_name | create_statement -------------+---------------------------------------------- t3 | CREATE TABLE t3 ( | ts TIMESTAMPTZ(3) NOT NULL, | a INT4 NULL | ) TAGS ( | ptag INT4 NOT NULL ) PRIMARY TAGS(ptag) | retentions 0s | activetime 1d (1 row)Show the
CREATE TABLEstatement for a table in a specified database.SHOW CREATE tsdb.t1;If you succeed, you should see an output similar to the following:
table_name | create_statement -----------------+---------------------------------------------- tsdb.public.t1 | CREATE TABLE t1 ( | ts TIMESTAMPTZ NOT NULL, | c1 INT4 NULL | ) TAGS ( | site INT4 NOT NULL ) PRIMARY TAGS(site) | retentions 0s | activetime 0s (1 row)
ALTER TABLE
The ALTER TABLE statement performs the following operations:
- Change the table name, set the retention and the zone configuration of the table.
- Add columns, change names, data type or width of columns, set the default values of columns, and remove default values of columns.
- Add tags, change names, data type or width of tags, and remove tags.
- Create partitions.
Note
- When removing a column from a table, you must ensure that there are at lease data columns in the table. In addition, you can not remove the first column (TIMESTAMP-typed column).
- Currently, KWDB does not support adding, removing, or renaming primary tags.
- Currently, KWDB does not support adding or removing multiple columns at once.
- When altering a table, KWDB will check whether the current table is referenced by any stream. If yes, the system ruturns an error and lists all streams that reference the specified table. In this case, you should remove the stream and then alter the table. For details about how to remove the stream, see DROP STREAM.
Privileges
Rename tables: the user must be a member of the
adminrole or have been granted theDROPprivilege on the specified table(s) and theCREATEprivilege on the specified database(s). By default, therootuser belongs to theadminrole.Add columns/tags to tables, update or rename columns/tags of tables, and remove columns/tags from tables: the user must be a member of the
adminrole or have been granted theCREATEprivilege on the specified table(s). By default, therootuser belongs to theadminrole.Set the retention of tables: the user must be a member of the
adminrole or have been granted theCREATEprivilege on the specified table(s). By default, therootuser belongs to theadminrole.Change the zone configurations of tables: the user must be a member of the
adminrole or have been granted theCREATEorZONECONFIGprivilege on the specified table(s). By default, therootuser belongs to theadminrole.Create partitions: the user must be a member of the
adminrole or have been granted theCREATEprivilege on the specified table(s). By default, therootuser belongs to theadminrole.
Syntax

Supported Operations
- ADD
ADD COLUMN: Add columns. You need to specify the column name and data type. You can set default values for columns. Each table supports up to 4096 columns.COLUMN: Optional. If not used, columns will be added by default.IF NOT EXISTS: Optional. When theIF NOT EXISTSkeyword is used, the system creates a new column only if a column of the same name does not already exist. Otherwise, the system fails to create a new column without returning an error. When theIF NOT EXISTSkeyword is not used, the system creates a new column only if a column of the same name does not already exist. Otherwise, the system fails to create a new column and returns an error.DEFAULT <default_expr>: Optional. Set a default value for a data column. For non-TIMESTAMP data columns, the default value must be a constant. For TIMESTAMP-typed columns, the default value can either be a constant or thenow()function. If the data type of the default value is not matched with that of the column, the system returns an error. KWDB supports setting NULL as the default value.NULL: Optional. It can be only set toNULL.
ADD TAG/ATTRITBUTE: Add tags. You need to specify the tag name and data type. Currently, KWDB does not support adding primary tags.
- ALTER
ALTER COLUMN: Change the data type or width of columns, as well as set or remove default values of columns.SET DATA: Optional. Whether or not using the keyword does not affect modifying the data type and width of the column.SET DEFAULT <default_expr>: Required. Set a default value for a data column. For non-TIMESTAMP data columns, the default value must be a constant. For TIMESTAMP-typed columns, the default value can either be a constant or thenow()function. If the data type of the default value is not matched with that of the column, the system returns an error. KWDB supports setting NULL as the default value.DROP DEFAULT: Required. Remove default values of columns. No default value is inserted after they are removed.
ALTER TAG/ATTRITBUTE: Change the data type or width of tags, where theSET DATAkeyword is optional. Whether or not using the keyword does not affect modifying the data type and width of the tag. Currently, KWDB does not support modifying the data type or width of primary tags. Note: If an index exists for the tag to be changed, you must delete the index first.
CONFIGURE ZONE: Change zone configurations of tables. For details, see Zones.- DROP
DROP COLUMN: Remove columns. You need to specify the column name.COLUMN: Optional. If not used, columns will be removed by default.IF EXISTS: Optional. When theIF EXISTSkeyword is used, the system removes the column only if the target table has already existed. Otherwise, the system fails to remove the column without returning an error. When theIF EXISTSkeyword is not used, the system removes the column only if the target table has already existed. Otherwise, the system fails to remove the column and returns an error.
DROP TAG/ATTRITBUTE: Remove tags. You need to specify the tag name. Currently, KWDB does not support removing primary tags. If an index exists for the tag to be deleted, you must delete the index first.
- PARTITION BY: Create table partitions. For details, see Partitions.
- RENAME
RENAME TO: Change the names of tables.RENAME COLUMN: Change the names of columns.RENAME TAG/ATTRIBUTE: Change the names of tags.
SET RETENTIONS: Set the retention of tables.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
table_name | The name of the table. You can use <database_name>.<table_name> to specify a table in another database. If not specified, use the table in the current database. |
column_name | The name of the column. The column name must be unique within the table and supports up to 128 bytes. |
data_type | The data type of the column. For details about the data types supported by a time-series table, see Time-Series Data Types. |
tag_name | The name of the tag. The tag name supports up to 128 bytes. KWDB does not support defining database-level tags. |
tag_type | The data type of the tag. It supports all numeric-typed, BOOL-typed, and STRING-typed data, except for NVARCHAR-typed data. |
new_type | The data type and data width of the column to modify. Note - The converted data width must be greater than the original data width. For example, INT4 can be converted to INT8 but not to INT2. CHAR(200) can be converted to VARCHAR (254) but not to VARCHAR (100). - CHAR-typed, VARCHAR-typed, NCHAR-typed, and NVARCHAR-typed values can be converted to values of the same data types. But the width cannot be shorter. For example, CHAR(100) can be converted to VARCHAR (200) but not to VARCHAR (50). For details about the data type, default width, maximum width, and convertible data types, see Time-Series Data Types. |
new_table_name | The new name of the table. It supports up to 128 bytes. |
old_name | The current name of the column or tag. Currently, KWDB does not support modifying names of primary tags. |
new_name | The new name of the column. The new name must be unique within the table and supports up to 128 bytes. |
keep_duration | Optional. Define the data retention period for the database. Data older than this duration will be automatically purged. Default: 0s (retain indefinitely)Time units: - Seconds: s or second- Minutes: m or minute- Hours: h or hour- Days: d or day- Weeks: w or week- Months: mon or month- Years: y or yearValid range: Positive integer up to 1000 years Note: - Table-level retention settings override database-level settings. - Longer retention periods consume more storage. Configure based on your business needs. - Data that already exceeds the retention period at write time will be rejected and not stored. |
Examples
This example performs the following operations on the ts_table table.
- Change the name and retention of the data.
- Add columns to the table, remove columns from the table, and change names and data types of columns.
- Add tags to the table, remove tags from the table, and change names and width of tags.
-- Rename the table.
ALTER TABLE ts_table RENAME TO tstable;
-- Change the retention of the table.
ALTER TABLE ts_table SET RETENTIONS = 20d;
-- Add a column to the table.
ALTER TABLE ts_table ADD COLUMN c3 INT NULL;
-- Add a column to the table and set a default value for the column.
ALTER TABLE ts_table ADD COLUMN c4 VARCHAR(50) DEFAULT 'aaa';
-- Remove a column from the table.
ALTER TABLE ts_table DROP c3;
-- Modify the name of a column.
ALTER TABLE ts_table RENAME COLUMN c2 TO c4;
-- Modify the data type of a column.
ALTER TABLE ts_table ALTER COLUMN c3 TYPE INT8;
-- Modify the default value of a column.
ALTER TABLE ts_table ALTER COLUMN c4 SET DEFAULT '789';
-- Remove the default value of a column.
ALTER TABLE ts_table ALTER COLUMN c4 DROP DEFAULT;
-- Add a tag to the table.
ALTER TABLE ts_table ADD TAG color VARCHAR(30);
-- Remove a tag from the table.
ALTER TABLE ts_table DROP TAG color;
-- Modify the name of a tag.
ALTER TABLE ts_table RENAME TAG site TO location;
-- Modify the width of a tag
ALTER TABLE ts_table ALTER color TYPE VARCHAR(50);
DROP TABLE
The DROP TABLE statement removes all tables from a database. After deletion, all privileges on the tables are also removed.
Note
When removing a table, KWDB will check whether the current table is referenced by any stream. If yes, the system ruturns an error and lists all streams that reference the specified table. In this case, you can use the CASCADE keyword to remove the specified table and its dependent objects.
Privileges
The user must be a member of the admin role or have been granted the DROP privilege on the specified table(s). By default, the root user belongs to the admin role.
Syntax
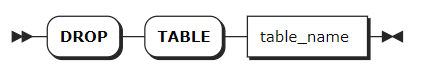
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
table_name | The name of the table. You can use <database_name>.<table_name> to specify a table in another database. If not specified, use the table in the current database. |
Examples
This example removes a table from the current database.
DROP TABLE ts_table;