Stored Procedures
In the KWDB database, a stored procedure is a database object which stores complex programs issued with a single CALL statement. Stored procedures are SQL statement sets to complete specific functions. They are compiled, created, and saved in the KWDB database. You can call stored procedures by specifying their names and parameters.
KWDB supports creating, modifying, checking, removing, and calling stored procedures. Stored procedures supports all SQL statements and the following special syntax:
DECLARESETSELECT,DELETE,INSERT,UPDATE INTO,UPSERTOPEN,FETCH,CLOSECONTINUE HANDLER,EXIT HANDLERIFELSELOOPLABELLEAVE- Transaction statements
- Special functions, such as (
ROW_COUNT())
Note
- Do not support nested stored procedures.
- Do not support calling stored procedures within explicit transactions.
- Do not support showing the execution plan of stored procedures using the
EXPLAIN(ANALYZE) statement. - Do not support referencing other database objects except for relational and time-series tables within a stored procedure.
- Do not support setting how to pass the values of parameters, such as
IN,OUT, orINOUT. All parameters are passed as input parameters. - If there are multiple results sets within a stored procedure and some result sets are empty, the empty result sets are not displayed.
- When connecting KWDB through the KaiwuDB JDBC Driver, only one result set is output in
PREPAREmode.
CREATE PROCEDURE
The CREATE PROCEDURE statement creates a stored procedure.
Privileges
The user must be a member of the admin role or have been granted the related privileges on the objects referenced within the stored procedure body (such as the SELECT privilege on the specified table). By default, the root user belongs to the admin role.
Syntax
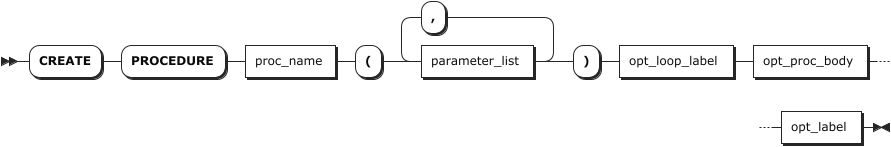
opt_proc_body

proc_set_stmt
proc_if_stmt

proc_while_stmt

simple_select_into_clause

proc_leave_stmt
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
proc_name | The name of the stored procedure to create. |
parameter_list | A comma-separated list of input parameter definitions of the stored procedure, in a format of var_name var_type. - var_name: the name of the variables. - var_type: the data type of the variables. Available options are INT2, INT4, INT8, FLOAT4, FLOAT8, DECIMAL, STRING, TEXT, CHAR, VARCHAR, TIMESTAMP, TIMESTAMPTZ. If not specified, it is set to NULL by default. |
opt_loop_label | The label of the stored procedure body, in a format of LABEL label_name:. |
opt_proc_body | The stored procedure body, including the SQL statements that must be executed when calling the stored procedure. The stored procedure body starts with the BEGIN keyword and ends with the END keyword. Note If you use KaiwuDB JDBC Driver to create a stored procedure, you should use the double dollars sign ( $$) to wrap the BEGIN ...END statement. |
opt_label | The label of the stored procedure body, in a format of label_name. The opt_loop_label and opt_label parameters must come in pairs. |
select_stmt | The SELECT statement to read data from the database. |
insert_stmt | The INSERT statement to insert one or more rows of data into tables. |
update_stmt | The UPDATE statement to update one row of data into tables. It is in a format of UPDATE .... RETURNING target_list INTO select_into_targets. |
upsert_stmt | The UPSERT statement to update and insert data into tables. |
delete_stmt | The DELETE statement to remove one row of data from tables. It is in a format ofDELETE FROM .... RETURNING target_list INTO select_into_targets. |
declare_stmt | The DECLARE statement to declare user-defined variables, handlers, and cursors. For details, see Declarations. |
proc_set_stmt | The SET statement to set values for user-defined variables or variables declared using the DECLARE statement. It is in a format of SET var_name = a_expr, where var_name refers to the name of the variable and a_expr refers to the expression of values applied to variables. User-defined variables set within a stored procedure are only valid for the current session. User-defined variables set within a stored procedure remain accessible and modifiable by the user in the external session after the stored procedure is called. Once the type of a user-defined variable is set within a stored procedure, do not support modifying its type. Subsequent assignments must be consistent with the initial type. Otherwise, the system returns an error. If a user-defined variable is set outside the stored procedure, when creating a stored procedure that sets a user-defined variable with the same name, the system checks whether a variable with the same name already exists. If it exists and the types are consistent, the variable is successfully set. Otherwise, the system returns an error. Note The value of a user-defined variable set within a stored procedure is not affected by COMMIT or ROLLBACK transaction statements. |
proc_if_stmt | The IF statement to execute various SQL statement blocks based on the specified condition. It is in a format of IF a_expr THEN proc_stmt_list opt_stmt_elsifs opt_stmt_else ENDIF. - a_expr: The conditional expression of the IF statement. a_expr must be an expression that returns Boolean values. - proc_stmt_list: The SQL statement to execute after the condition is met. The SQL statements supported by the IF statement are identical to those supported by the CREATE PROCEDURE statement. - opt_stmt_elsifs: Optional. Other conditions of the IF statement. - opt_stmt_else: Optional. The ELSE condition of the IF statement. |
proc_while_stmt | The WHILE statement to repeatedly execute codes when the specified condition is met. It is in a format of opt_loop_label WHILE a_expr DO proc_stmt_list ENDWHILE opt_label. - opt_loop_label: The label of the WHILE statement. - a_expr: The conditional expression of the WHILE statement. - proc_stmt_list: The SQL statement to execute after the condition is met. The SQL statements supported by the WHILE statement are identical to those supported by the CREATE PROCEDURE statement. - opt_label: The label of the WHILE statement, in a format of label_name. The opt_loop_label and opt_label parameters must come in pairs. |
begin_stmt | The statement to begin a transaction. |
commit_stmt | The statement to commit a transaction. |
rollback_stmt | The statement to roll back a transaction. |
simple_select_into_clause | The simple select statement in a format of SELECT .... INTO select_into_targets from_clause ..... select_into_targets: Support inserting a comma-separated list of variables, including user-defined variables. |
declare_cursor_stmt | The statement to declare a cursor. For details, see Declare Cursors. |
open_cursor_stmt | The statement to open a cursor. For details, see OPEN. |
fetch_cursor_stmt | The statement to fetch a cursor. For details, see FETCH. |
close_cursor_stmt | The statement to close a cursor. For details, see CLOSE. |
proc_leave_stmt | When using the LABEL keyword to define labels for the stored procedure body or WHILE statement, you can use the LEAVE statement to step out the stored procedure body or the WHILE loop. It is in a format of LEAVE label_name. |
prepare_stmt | The PREPARE statement in a format of PREPARE stmt_name AS stmt_sql. The name of a PREPARE statement must be globally unique within the current session. When creating a PREPARE statement within a stored procedure, if its name duplicates an existing PREPARE statement, the system returns an error. PREPARE statements created within a stored procedure are only valid for the current session and are automatically cleaned up after the session ends. Within a stored procedure, the SQL statement defined in a PREPARE statement must be a single complete SQL statement supported by the stored procedure. Parameter placeholders in the SQL statement only support the dollar sign ($) and can only replace values in the SQL (e.g., WHERE id = $1). They cannot replace identifiers such as table names, column names, or keywords. Within a stored procedure, PREPARE statements support SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, UPSERT, and DELETE statements. Within a stored procedure, PREPARE statements do not support transaction statements (BEGIN, START TRANSACTION, COMMIT, and ROLLBACK), session control statement (USE), flow control statements of stored procedures, stored procedure-related statements (CREATE PROCEDURE, ALTER PROCEDURE, DROP PROCEDURE, CALL PROCEDURE), SELECT INTO statements, or DDL statements. PREPARE statements defined outside a stored procedure can be used within the stored procedure. Conversely, if the system does not actively release a PREPARE statement created within a stored procedure, that PREPARE statement can also be used outside the stored procedure.Note - Do not support nested PREPARE statements (one PREPARE statement inside another).- The PREPARE statements cannot include temporary variables (declared using the DECLARE statement) or user-defined variables defined within the stored procedure. - After executing a PREPARE statement, if the DEALLOCATE PREPARE statement is not explicitly executed, the prepared object remains in the current session. In this case, if a prepared object with the same name is created outside the stored procedure, the system returns an error. |
execute_stmt | The EXECUTE statement in a format of EXECUTE stmt_name para_value. Note The EXECUTE statements cannot include temporary variables (declared using the DECLARE statement) or IN parameters defined within the stored procedure. You need to convert them using the SET @var = variable statement. |
deallocate_stmt | The DEALLOCATE statement in a format of DEALLOCATE PREPARE stmt. To remove all PREPARE statements, use the DEALLOCATE ALL or DEALLOCATE PREPARE ALL statement. |
Examples
Create a stored procedure.
This example creates a stored procedure named
test.-- Set the delimiter to double backslash. delimiter \\ -- Create a stored procedure. create procedure test() label test: begin declare a int; declare b int; declare err int; declare exit HANDLER FOR NOT FOUND,SQLEXCEPTION BEGIN SET err = -1; SELECT a,b; ROLLBACK; ENDHANDLER; START TRANSACTION; set a = 10; select a, b from t1; update t1 set a = a + 1 where b > 0; insert into t1 values (a, b); label my_loop: WHILE b <= 10 DO declare d int; set d = b + 2; if d > 9 then select * from t1; leave my_loop; elsif b > 5 then select * from t2; endif; set b = b + 1; ENDWHILE my_loop; IF err = 0 THEN SELECT a,b; ENDIF; COMMIT; end test\\ delimiter ; CREATE PROCEDURECreate a stored procedure and set user-defined variables within the stored procedure.
-- Set the delimiter to double backslash. DELIMITER \\ -- Create a stored procedure. CREATE PROCEDURE proc1() BEGIN declare a int; set a = 10; set @b = 1; select @b; set @b = a; select @b; END // CREATE PROCEDURE Time: 60.4819msCreate a stored procedure and use the
PREPARE,EXECUTE, andDEALLOCATEstatements.-- Set the delimiter to double backslash. DELIMITER \\ -- Create a stored procedure.s CREATE PROCEDURE proc1() BEGIN PREPARE stmt as SELECT 1; EXECUTE stmt; DEALLOCATE PREPARE stmt; END // CREATE PROCEDURE Time: 60.4819ms
CALL
The CALL statement calls a stored procedure.
Note
- If user-defined variables are defined when creating a stored procedure, the system checks whether a user-defined variable with the same name already exists outside the stored procedure when the procedure is called. If it exists and the types are consistent, the system will successfully call the stored procedure and overwrite the original value with the new user-defined variable value. Otherwise, the system returns an error.
- If a
PREPAREstatement is defined when creating a stored procedure, the system checks the syntax of thePREPAREstatement when the procedure is called. If the syntax is invalid, the system returns an error. - If the execution of a
PREPAREstatement is defined when creating a stored procedure, the system checks whether the object of thePREPAREstatement to be executed exists when the procedure is called. If it does not exist, the system returns an error. - If the deallocation of a
PREPAREstatement is defined when creating a stored procedure, the system checks whether the object of thePREPAREstatement to be deallocated exists when the procedure is called. If it does not exist, the system returns an error.
Privileges
The user must be a member of the admin role or have been granted the EXECUTE privilege on the specified stored procedure(s) and related privileges on the objects referenced within the stored procedure body (such as the SELECT privilege on the specified table). By default, the root user belongs to the admin role.
Syntax

Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
proc_name | The name of the stored procedure to call. |
input_param_list | A comma-separated list of input parameter definitions of the stored procedure. Note When calling a stored procedure, the number, order, and type of specified input parameters must match with those specified when creating the stored procedure. |
Examples
This example calls a stored procedure named test1 to check the data in the stored procedure when the a parameter is set to 1.
-- Set the delimiter to double backslash.
DELIMITER \\
-- Create a stored procedure.
CREATE PROCEDURE test1(a int)
label test:
begin
if a > 5 then
select a;
else
select 5,4,3,2,1;
endif;
end test \\
-- Set the delimiter to semicolon.
DELIMITER ;
-- Call the stored procedure.
call test1(1);
?column? | ?column? | ?column? | ?column? | ?column?
-----------+----------+----------+----------+-----------
5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1
ALTER PROCEDURE
The ALTER PROCEDURE statement modifies comments of a specified stored procedure. You can also use the COMMENT ON statement to modify the comments of the specified stored procedure. For details, see COMMENT ON.
Privileges
The user must be a member of the admin role or have been granted the CREATE privilege on the specified stored procedure(s). By default, the root user belongs to the admin role.
Syntax

Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
proc_name | The name of the stored procedure to modify. |
comment_text | The comment to be associated to the stored procedure. |
Examples
This example adds comments to the proc1 stored procedure.
ALTER PROCEDURE proc1 COMMENT IS 'test query sql and if else logical';
SHOW PROCEDURES
The SHOW PROCEDURES statement lists all created stored procedures in the current KWDB database.
The SHOW CREATE PROCEDURE statement shows the CREATE PROCEDURE statement for an existing stored procedure and the parameters specified when creating the stored procedure.
Privileges
The user must have any privilege on the specified stored procedure(s).
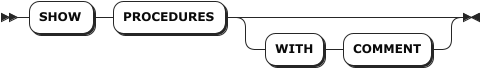
Syntax
Show all created stored procedures
Show the
CREATE PROCEDUREstatement for an existing stored procedure
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
WITH COMMENT | Optional. Show a stored procedure's comments. |
proc_name | The name of the stored procedure to show. |
Examples
Show all created stored procedures in the current KWDB database.
SHOW PROCEDURES; procedure_name ------------------ proc1 (1 row)Show all created stored procedures with comments in the current KWDB database.
SHOW PROCEDURES WITH COMMENT; procedure_name | comment -----------------+------------------------------------- proc1 | test query sql and if else logical (1 row)Show the
CREATE PROCEDUREstatement for a specified stored procedure.SHOW CREATE PROCEDURE proc1; procedure_name | procedure_body -----------------+------------------------------------------------------- proc1 | CREATE PROCEDURE proc1() | BEGIN | DECLARE a INT4; | DECLARE b INT4; | DECLARE err INT4; | DECLARE EXIT HANDLER FOR NOT FOUND,SQLEXCEPTION | BEGIN | SET err = -1; | SELECT a, b; | ROLLBACK TRANSACTION; | ENDHANDLER; | BEGIN TRANSACTION; | SET a = 10; | SELECT a, b FROM test.public.t1; | UPDATE test.public.t1 SET a = a + 1 WHERE b > 0; | INSERT INTO test.public.t1 VALUES (a, b); | LABEL my_loop: | WHILE b <= 10 DO | DECLARE d INT4; | SET d = b + 2; | IF d > 9 THEN | SELECT t1.a, t1.b FROM test.public.t1; | LEAVE my_loop; | ELSIF b > 5 THEN | SELECT t2.a, t2.b, t2.c FROM test.public.t2; | ENDIF; | SET b = b + 1; | ENDWHILE my_loop; | IF err = 0 THEN | SELECT a, b; | ENDIF; | COMMIT TRANSACTION; | END (1 row)
DROP PROCEDURE
The DROP PROCEDURE statement removes a stored procedure.
Privileges
The user must be a member of the admin role or have been granted the DROP privilege on the specified stored procedure(s). By default, the root user belongs to the admin role.
Syntax

Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
IF EXISTS | Optional. - When the IF EXISTS keyword is used, the system removes the stored procedure only if the stored procedure has already existed. Otherwise, the system fails to remove the stored procedure without returning an error. - When the IF EXISTS keyword is not used, the system removes the stored procedure only if the stored procedure has already existed. Otherwise, the system fails to remove the stored procedure and returns an error. |
proc_name | The name of the stored procedure to remove. |
Examples
This example removes the proc1 stored procedure.
DROP PROCEDURE proc1;