Relational Databases
CREATE DATABASE
The CREATE DATABASE statement creates a relational database.
Privileges
The user must be a member of the admin role. By default, the root user belongs to the admin role.
Syntax
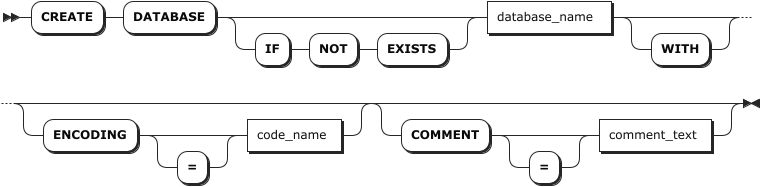
Parameters
Note
The optional parameters must be configured in an order of [ENCODING [=] <'code_name'>] [COMMENT [=] <'comment_text'>]. Otherwise, the system returns an error.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
IF NOT EXISTS | Optional. - When the IF NOT EXISTS keyword is used, the system creates a new database only if a database of the same name does not already exist. Otherwise, the system fails to create a new database without returning an error. - When the IF NOT EXISTS keyword is not used, the system creates a new database only if a database of the same name does not already exist. Otherwise, the system fails to create a new database and returns an error. |
db_name | The name of the database to create, which must be unique and follow these Identifier Rules. |
WITH | Optional. Whether or not using the keyword does not affect the creation of the database. |
ENCODING | Optional. Specify the encoding method. Currently, KWDB only supports UTF-8 and its alias (UTF8 and UNICODE). Values should be enclosed in single quotes (' ') and are case-insensitive, such as CREATE DATABASE bank ENCODING = 'UTF-8'. |
COMMENT | Optional. Specify the comment to be associated to the database. |
Examples
Create a database.
This example creates a database named
db1.CREATE DATABASE db1; CREATE DATABASECreate a database using the
IF NOT EXISTSkeyword.This example creates a database named
db1, which has already existed. The system fails to create the database without returning an error.CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS db1; CREATE DATABASECreate a database and specify comments for the database.
This example creates a database named
db_studentand associates the comment textdatabase for student statisticsto the database.CREATE DATABASE db_student COMMENT = 'database for student statistics';
SHOW DATABASES
The SHOW DATABASES statement lists all databases in the KWDB cluster, including relational databases and time-series databases.
Privileges
N/A
Syntax
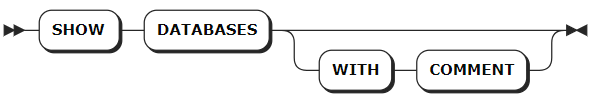
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
WITH COMMENT | Optional. Show a database's comments. By default, the database's comment is set to NULL. |
Examples
Note
The engine_type for time-series databases and relational databases is TIME SERIES and RELATIONAL respectively.
Show all created databases.
SHOW DATABASES;If you succeed, you should see an output similar to the following:
database_name | engine_type ----------------+-------------- db1 | RELATIONAL db2 | RELATIONAL defaultdb | RELATIONAL postgres | RELATIONAL system | RELATIONAL iot | TIME SERIES (6 rows)Show all created databases' comments.
SHOW DATABASES WITH COMMENT;If you succeed, you should see an output similar to the following:
database_name | engine_type | comment ----------------+-------------+---------- db1 | RELATIONAL | NULL db2 | RELATIONAL | NULL defaultdb | RELATIONAL | NULL postgres | RELATIONAL | NULL system | RELATIONAL | NULL iot | TIME SERIES | NULL (6 rows)
SHOW CREATE DATABASE
The SHOW CREATE DATABASE statement shows the CREATE DATABASE statement for an existing database. Currently, the relational database only supports viewing the name of the database.
Privileges
N/A
Syntax

Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
database_name | The name of the database to view. |
Examples
This example shows the statement that is used to create the reldb1 database.
-- 1. Create a database named reldb1.
CREATE DATABASE reldb1 WITH ENCODING = 'UTF8';
--2. Show the created reldb1 database.
SHOW CREATE DATABASE reldb1;
database_name | create_statement
----------------+-------------------------
reldb1 | CREATE DATABASE reldb1
(1 row)
ALTER DATABASE
The ALTER DATABASE statement modifies the database name or zone configuration.
Note
KWDB does not support changing the name of a database which has dependent views.
Privileges
- Modify database name: The user must be a member of the
adminrole. By default, therootuser belongs to theadminrole. - Modify system database zone configuration: The user must be a member of the
adminrole. By default, therootuser belongs to theadminrole. - Modify other database zone configuration: The user must be a member of the
adminrole or have CREATE or ZONECONFIG privileges on the target database. By default, therootuser belongs to theadminrole.
Syntax

Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
database_name | The name of the database to change. If the target database is the current database, set the sql_safe_updates parameter to true. Otherwise, the database cannot be renamed. |
new_name | The new name of the database, which must be unique and follow these Identifier Rules. |
variable | The name of the variable to modify. The following variables are supported: - range_min_bytes: the minimum size in bytes for a data range. When a range is smaller than this value, KWDB merges it with an adjacent range. Default: 256 MiB. The value must be greater than 1 MiB (1048576 bytes) and smaller than the maximum size of the range. - range_max_bytes: the maximum size in bytes for a data range. When a range exceeds this value, KWDB splits it into two ranges. Default: 512 MiB. The value must not be smaller than 5 MiB (5242880 bytes). - gc.ttlseconds: the number of seconds data will be retained before garbage collection. Default: 90000 (25 hours). We recommend setting a value of at least 600 seconds (10 minutes) to avoid affecting long-running queries. A smaller value saves disk space while a larger value increases the time range allowed for AS OF SYSTEM TIME queries. Additionally, since all versions of each row are stored in a single, unsplit range, avoid setting this value too large to prevent all changes to a single row from exceeding 64 MiB, which may cause memory issues or other problems. - num_replicas: the number of replicas. Default: 3. For the system database and the meta, liveness, and system ranges, the default number of replicas is 5. Note: The number of replicas cannot be reduced when unavailable nodes exist in the cluster. - constraints: required (+) and/or prohibited (-) constraints for where replicas can be placed. For example, constraints = '{"+region=NODE1": 1, "+region=NODE2": 1, "+region=NODE3": 1}' places one replica on each of nodes 1, 2, and 3. Currently only supports the region=NODEx format. - lease_preferences: an ordered list of required (+) and/or prohibited (-) constraints for where the leaseholder should be placed. For example, lease_preferences = '[[+region=NODE1]]' prefers placing the leaseholder on node 1. If this isn't possible, KWDB tries the next preference in the list. If no preferences can be satisfied, KWDB uses the default lease distribution algorithm, which balances leases across nodes based on their current lease count. Each value in the list can contain multiple constraints. |
value | The value of the variable to change. |
COPY FROM PARENT | Use the settings of the parent zone. |
DISCARD | Remove the zone settings and use the default values. |
Examples
Change the name of a database.
This example renames the
rdbdatabase torelationaldb.-- 1. Show all databases. SHOW DATABASES; database_name|engine_type -------------+----------- defaultdb |RELATIONAL postgres |RELATIONAL rdb |RELATIONAL system |RELATIONAL tsdb |TIME SERIES (5 rows) -- 2. Rename the rdb database to relationaldb. ALTER DATABASE rdb RENAME TO relationaldb; ALTER DATABASE -- 3. Show all databases. SHOW DATABASES; database_name|engine_type -------------+----------- defaultdb |RELATIONAL postgres |RELATIONAL relationaldb |RELATIONAL system |RELATIONAL tsdb |TIME SERIES (5 rows)Change the zone configurations of a database.
This example sets the number of the replicas of the
db3database to5and the time to retain data before garbage collection to100000seconds.-- 1. Change the zone configurations of the tsdb database. ALTER DATABASE db3 CONFIGURE ZONE USING num_replicas = 5, gc.ttlseconds = 100000; CONFIGURE ZONE 1 -- 2. Check whether the configurations are applied successfully. SHOW ZONE CONFIGURATION FOR DATABASE db3; target | config_sql -------------------+------------------------------------------ DATABASE db3 | ALTER DATABASE db3 CONFIGURE ZONE USING | range_min_bytes = 134217728, | range_max_bytes = 536870912, | gc.ttlseconds = 100000, | num_replicas = 5, | constraints = '[]', | lease_preferences = '[]' (1 row)
DROP DATABASE
The DROP DATABASE statement removes a database and all its objects from a KWDB cluster. To remove the current database, use the USE <database_name> statement to set another database as the current database. After deletion, all privileges on the database and its tables are also removed.
Privileges
The user must be a member of the admin role or have DROP privileges on the target database and objects. By default, the root user belongs to the admin role.
Syntax
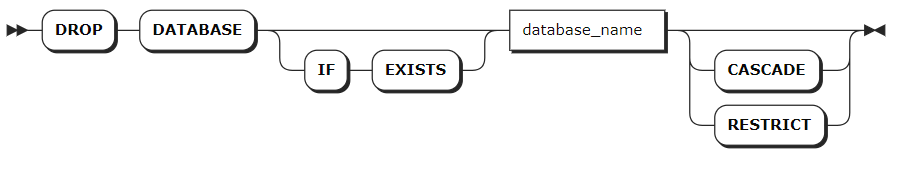
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
IF EXISTS | Optional. - When the IF EXISTS keyword is used, the system removes the database only if the database has already existed. Otherwise, the system fails to remove the database without returning an error. - When the IF EXISTS keyword is not used, the system removes the database only if the database has already existed. Otherwise, the system fails to remove the database and returns an error. |
database_name | The name of the database to remove. |
CASCADE | Optional. Remove tables and views in the database as well as all objects (such as constraints and views) that depend on those tables. The CASCADE keyword does not list objects it removes, so it should be used cautiously. |
RESTRICT | Optional. Do not remove the database if it contains any tables or views. |
Examples
Remove a database and its dependent objects using the
CASCADEkeyword.-- 1. Show tables in the relationaldb database. SHOW TABLES FROM relationaldb; table_name|table_type ----------+---------- ints |BASE TABLE (1 row) -- 2. Remove the relationaldb database and its dependent objects. DROP DATABASE relationaldb CASCADE; DROP DATABASE -- 3. Show tables in the relationaldb database. SHOW TABLES FROM relationaldb; ERROR: target database or schema does not existRemove a database and its dependent objects using the
RESTRICTkeyword.-- 1. Show tables in the db1 database. SHOW TABLES FROM db1; table_name|table_type ----------+---------- int |BASE TABLE ints |BASE TABLE (2 rows) -- 2. Remove the db1 database. DROP DATABASE db1 RESTRICT; ERROR: database "db1" is not empty and RESTRICT was specified