Queries
SHOW QUERIES
The SHOW QUERIES statement lists details about currently active SQL queries.
Privileges
- Members of the
adminrole (By default, therootuser belongs to theadminrole.): view any currently active queries. - Users who are not members of the
adminrole: view only their own currently active queries.
Syntax
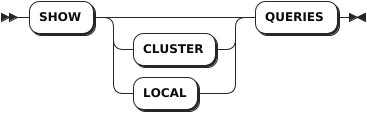
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
CLUSTER | Optional. List the active queries across all nodes of the cluster. |
LOCAL | Optional. List the active queries on the local node. |
Responses
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
query_id | The ID of the query. |
node_id | The ID of the node. |
session_id | The ID of the session. |
user_name | The name of the connected user. |
start | The timestamptz at which the query starts. |
query | The SQL query statement. |
client_address | The address and port of the client that issues the SQL query. |
application_name | The application name specified by the client, if any. |
distributed | Whether to execute the query distributedly. |
phase | The phase of the query's execution. Available options: - prepare: the statement is being parsed and planned.- executing: the statement is being executed. |
exec_progress | The execution process for a query on the executing phase. |
Examples
List the active queries across all nodes of the cluster.
SHOW QUERIES;If you succeed, you should see an output similar to the following:
query_id | node_id | session_id | user_name | start | query | client_address | application_name | distributed | phase | exec_progress -----------------------------------+---------+----------------------------------+-----------+----------------------------------+----------------------+------------------+------------------+-------------+-----------+---------------- 17c9796fa28ec8a10000000000000001 | 1 | 17c962175c4579860000000000000001 | root | 2024-04-25 08:44:13.566642+00:00 | SHOW CLUSTER QUERIES | 172.18.0.1:47104 | $ kwbase sql | false | executing | 0 (1 row)List the active queries on the local node.
SHOW LOCAL QUERIES;If you succeed, you should see an output similar to the following:
query_id | node_id | session_id | user_name | start | query | client_address | application_name | distributed | phase | exec_progress -----------------------------------+---------+----------------------------------+-----------+----------------------------------+--------------------+------------------+------------------+-------------+-----------+---------------- 17c9796c44bef85c0000000000000001 | 1 | 17c962175c4579860000000000000001 | root | 2024-04-25 08:43:59.107805+00:00 | SHOW LOCAL QUERIES | 172.18.0.1:47104 | $ kwbase sql | false | executing | 0 (1 row)
CANCEL QUERY
The CANCEL QUERY statement cancels a running SQL query.
Note
- Schema changes are treated differently than other SQL queries. You can use the
SHOW JOBSstatement to monitor the progress of schema changes and theCANCEL JOBstatement to cancel schema changes that are taking longer than expected. - In rare cases where a query is close to completion when a cancellation request is issued, the query may run to completion.
Privileges
- Members of the
adminrole (By default, therootuser belongs to theadminrole.): cancel any currently active queries. - Users who are not members of the
adminrole: cancel only their own currently active queries.
Syntax
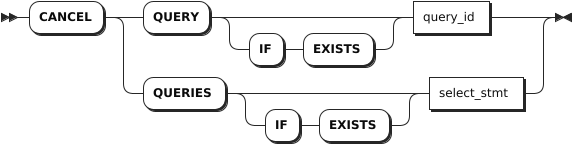
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
IF EXISTS | Optional. - When the IF EXISTS keyword is used, the system cancels a query only if the target query has already existed. Otherwise, the system fails to cancel the query without returning an error. - When the IF EXISTS keyword is not used, the system cancels a query only if the target query has already existed. Otherwise, the system fails to cancel the query and returns an error. |
query_id | The ID of the query to cancel. |
select_stmt | A selection query whose result you want to cancel. |
Note
The CANCEL QUERY statement accepts a single query ID. If a subquery is used and returns multiple query IDs, the CANCEL QUERY statement will fail. To cancel multiple queries, use the CANCEL QUERIES statement.
Examples
Cancel a query through the query ID.
-- 1. Use the SHOW QUERIES statement to get the ID of a query. SHOW QUERIES; query_id | node_id | session_id | user_name | start | query | client_address | application_name | distributed | phase | exec_progress -----------------------------------+---------+----------------------------------+-----------+----------------------------------+----------------------+------------------+------------------+-------------+-----------+---------------- 17c9796fa28ec8a10000000000000001 | 1 | 17c962175c4579860000000000000001 | root | 2024-04-25 08:44:13.566642+00:00 | SHOW CLUSTER QUERIES | 172.18.0.1:47104 | $ kwbase sql | false | executing | 0 (1 row) -- 2. Cancel the query based on the query ID. CANCEL QUERY '17c9796fa28ec8a10000000000000001'; CANCAL QUERIES 1Cancel a query through a subquery.
CANCEL QUERY (SELECT query_id FROM [SHOW CLUSTER QUERIES] WHERE client_address='your-host-ip:port' AND user_name='root' AND query = 'SHOW CLUSTER QUERIES'); CANCAL QUERIES 1