INSERT
The INSERT statement inserts data to specified tables, including:
- Insert one or more rows into a time-series table.
- Use the
SELECTclause to insert query results of another time-series table into the specified time-series table or relational table. - Use the
SELECTclause to insert cross-model query results into the specified time-series table.
Note
- KWDB supports out-of-order data writes. By default, query results are returned in the order of data insertion. To sort the returned data, use the
ORDER BYclause in your query and specify the sorting condition. - KWDB deduplicates data with identical timestamps. By default, newly written data overwrites existing data with the same timestamp. You can configure deduplication rules using the
SET CLUSTER SETTING ts.dedup.rule=[ merge | override | discard]statement. For details, see Real-Time Parameters. - When inserting cross-model query results into a specified time-series table using the
SELECTclause, the system returns an error"first column must be timestamp when the target table is table of time series" if the first column is not a timestamp-typed column.
Privileges
- Insert data into the table: the user must be a member of the
adminrole or have been granted theINSERTprivilege on the specified table(s). - Insert query results of other time-series tables into the table: the user must be a member of the
adminrole or have been granted theINSERTprivilege on the specified table(s) and theSELECTprivilege on other time-series table(s).
Syntax
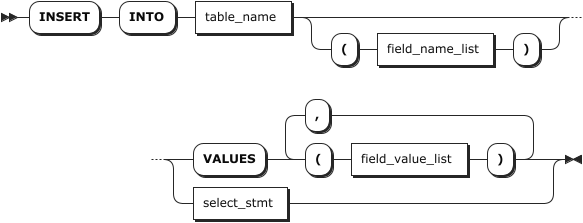
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
table_name | The name of the table. You can use <database_name>.<table_name> to specify a table in another database. If not specified, use the table in the current database. |
field_name_list | An optional comma-separated list of data columns and tag columns. - When column names are specified, you can specify all or a subset of the data columns or tag columns in the target table, and their order can differ from the table's defined column order. The specified columns must include the first column (timestamp-typed column) and all Primary Tag columns. If only tag columns are specified, the system will add tag values based on the written data. - When no column names are specified, data and tag values are written in the order defined in the table definition. For unspecified columns, if the column allows null values, the system automatically fills it with NULL. Otherwise, the system returns the Null value in column %s violates not-null constraints error. |
field_value_list | A comma-separated list of data values and tag values. - When column names are specified, data values and tag values are inserted into the table based on the defined column order. The data type and number of the inserted data must match the defined data type and the number of specified columns. - When no column names are specified, data and tag values are written in the order defined in the table definition. The data type and number of the inserted data must match the defined data type and the number of specified columns. - The inserted data must include the timestamp-typed data and Primary Tag values. You can use the NOW() function to get the server's current time (precision: millisecond) or use the time sting or INT64 data type to represent the timestamp (unit: millisecond). - When inserting multiple rows, if a Primary Tag value corresponds to different common tag values, the system will use the Primary Tag value and common tag value, which are inserted at first, to replace common tag values related to the Primary Tag value. |
select_stmt | The SELECT statement. For details, see SELECT. The number of columns returned by the SELECT statement must be consistent with the number of columns inserted by the INSERT INTO statement. Note Currently, KWDB does not support inserting duplicate columns or data of a specified table, such as INSERT INTO t1 SELECT c1, c1 from t0 or SELECT 0,0 from t0. |
Examples
Insert a single row without specifying column names.
INSERT INTO ts_table VALUES ('2023-07-13 14:06:32.272', 10.2, 219, 0.32, 1,1);Insert multiple rows without specifying column names.
INSERT INTO ts_table2 VALUES ('2023-07-13 14:06:32.272', 10.2, 219, 0.32,1,1), ('2023-07-13 14:06:32.272', 10.15, 217, 0.33,2,0);Insert a single row by specifying column names and using use the defined column order.
INSERT INTO ts_table (k_timestamp, e1, e2, e3, id) VALUES ('2023-07-13 14:06:32.272', 10.2, 219, 0.32, 1);Insert a single row by specifying column names but do not use the defined column order.
INSERT INTO ts_table (e1, e2, e3, id, k_timestamp) VALUES (10.2, 219, 0.32, 1,'2023-07-13 14:06:32.272');Insert multiple rows by specifying some column names.
INSERT INTO ts_table (k_timestamp, e1,id) VALUES (now(), 10.2,1), ('2023-07-13 14:06:32.272', 10.15,2), (1681972496619, 10.4,3);Insert query results of other time-series tables into the specified time-series table.
INSERT INTO ts_table SELECT * FROM temperature;Insert query results of other time-series tables into the specified relational table.
INSERT INTO test.test1 SELECT * FROM test_ts.ts_table;Insert cross-model query results into the specified time-series table.
-- successful response INSERT INTO test_ts.ts_table2 SELECT t2.time,t1.col1,t1.col2,t2.e3,t2.e4,t2.e5,t2.e6,t2.attr1 FROM test.test1 AS t1 JOIN test_ts.ts_table AS t2 ON t2.e1=t1.col1; -- error: first column must be timestamp when the target table is table of time series INSERT INTO test_ts.ts_table2 SELECT t2.e1, t1.col1,t1.col2,t2.e3,t2.e4,t2.e5,t2.e6,t2.attr1 FROM test.test1 AS t1 JOIN test_ts.ts_table AS t2 ON t2.e1=t1.col1;