SELECT Optimization
KWDB supports using EXPLAIN or EXPLAIN ANALYZE output to optimize your queries as follows:
- The less levels are, the more quickly queries execute.
- Restructure queries to require fewer levels of processing and then improve performance. Avoid scanning an entire table, which is the slowest way to access data. Create indexes that contain at least one of the columns that the query is filtering in its
WHEREclause.
EXPLAIN
The EXPLAIN statement returns KWDB's statement plan for a preparable statement. You can use this information to optimize the query.
Privileges
The user must be a member of the admin role or have been granted appropriate privileges for the statement being explained.
Syntax
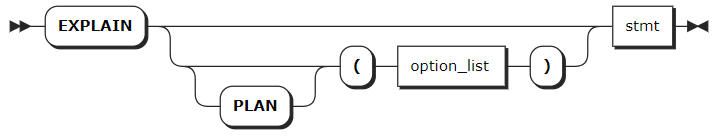
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
option_list | An optional comma-separated list of options. KWDB supports the following options: - VERBOSE: show as much information as possible about the statement plan. - TYPES: include the data types KWDB chooses to evaluate intermediate SQL expressions. - OPT: display the statement plan tree generated by the Cost-Based Optimizer (COB). |
stmt | The SELECT statement to explain. |
Responses
A successful EXPLAIN statement returns a table with the following fields:
tree: a tree representation of the hierarchy of the statement plan.field: the property names of the statement plan. Distributed and vectorized properties apply to the entire statement plan while other properties apply to statement plan nodes in the tree architecture.description: additional information about parameters in fields.columns: the columns provided to processes at lower levels of the hierarchy. This field is included in output of theEXPLAINstatement with theTYPESorVERBOSEoption.ordering: the order where the results are presented to processes at each level of the hierarchy and other attributes of the result set at each level. This field is included in output of theEXPLAINstatement with theTYPESorVERBOSEoption.
Examples
These examples assume that you have created a table and inserted data into the table.
-- 1. Create a table named t3.
CREATE TABLE t3(k_timestamp timestamp not null,e1 int) TAGS (c1 smallint not null,c2 nchar(10) not null,c3 char not null,c4 varchar(10) not null,size int not null) PRIMARY TAGS (c1,c2,c3,c4);
-- 2. Insert data into the table.
INSERT INTO t3 VALUES ('2024-1-1 1:00:00',1,1,'100','a','aa',2);
INSERT INTO t3 VALUES ('2024-1-1 1:01:00',2,2,'200','a','aaa',2);
INSERT INTO t3 VALUES ('2024-1-1 2:00:00',3,2,'200','a','aaa',6);
INSERT INTO t3 VALUES ('2024-1-1 3:00:00',4,4,'500','b','bb',4);
INSERT INTO t3 VALUES ('2024-1-1 4:00:00',5,5,'500','b','bb',5);
INSERT INTO t3 VALUES ('2024-1-1 5:00:00',6,6,'6','b','bbb',6);
INSERT INTO t3 VALUES ('2024-1-1 6:00:00',7,7,'8','c','cc',7);
INSERT INTO t3 VALUES ('2024-1-1 7:00:00',8,8,'8','c','cc',8);
INSERT INTO t3 VALUES ('2024-1-1 8:00:00',9,9,'9','c','cc',9);
INSERT INTO t3 VALUES ('2024-1-1 9:00:00',10,10,'10','c','ccc',10);
Run the
EXPLAINstatement without any parameters.EXPLAIN SELECT c1 FROM t3 WHERE c1 = 1; tree | field | description ---------------+---------------+----------------- | distributed | true | vectorized | false synchronizer | | └── ts scan | | | ts-table | t3 | access mode | tableTableMeta | tag filter[0] | c1 = 1 (7 rows)Run the
EXPLAINstatement with theVERBOSEoption.EXPLAIN (VERBOSE) SELECT c1 FROM t3 WHERE c1 = 1; tree | field | description | columns | ordering ---------------+---------------+----------------+---------+----------- | distributed | true | | | vectorized | false | | synchronizer | | | (c1) | └── ts scan | | | (c1) | | ts-table | t3 | | | access mode | tableTableMeta | | | tag filter[0] | c1 = 1 | | (7 rows)Run the
EXPLAINstatement with theTYPESoption.EXPLAIN (TYPES) SELECT c1 FROM t3 WHERE c1 = 1; tree | field | description | columns | ordering ---------------+---------------+-------------------------------+-----------+----------- | distributed | true | | | vectorized | false | | synchronizer | | | (c1 int2) | └── ts scan | | | (c1 int2) | | ts-table | t3 | | | access mode | tableTableMeta | | | tag filter[0] | ((c1)[int2] = (1)[int])[bool] | | (7 rows)Run the
EXPLAINstatement with theOPToption.EXPLAIN (OPT) SELECT c1 FROM t3 WHERE c1 = 1; text ------------ t-s-scan (1 row)Run the
EXPLAINstatement with theOPTandVERBOSEoptions.EXPLAIN (OPT,VERBOSE) SELECT c1 FROM t3 WHERE c1 = 1; text ---------------------------------------------------- t-s-scan ├── columns: c1:3 ├── stats: [rows=8, distinct(3)=0.8, null(3)=0] ├── cost: 0.01 └── fd: ()-->(3) (5 rows)
EXPLAIN ANALYZE
The EXPLAIN ANALYZE statement executes a SQL query and generates a statement plan with execution statistics. Statement plans provide information around SQL execution, which can be used to troubleshoot slow queries by figuring out where time is being spent, how long a component takes streams of input rows and processes them according to a specification, etc.
Privileges
The user must be a member of the admin role or have been granted appropriate privileges for the statement being explained.
Syntax

preparable_stmt
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
preparable_stmt | The statement you want details about. Basically, all preparable statements can work with EXPLAIN ANALYZE, such as CREATE, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE and so on. |
Examples
This example runs a SELECT query using the EXPLAIN ANALYZE statement.
EXPLAIN ANALYZE(DEBUG) SELECT * FROM accounts WHERE id > 2 ORDER BY balance DESC;
text
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Statement diagnostics bundle generated. Download FROM the Admin UI (Advanced
Debug -> Statement Diagnostics History), via the direct link below, or using
the command line.
Admin UI: http://127.0.0.1:8080
Direct link: http://127.0.0.1:8080/_admin/v1/stmtbundle/857952323520757761
Command line: kwbase statement-diag list / download
(6 rows)